Maldives Becomes First Nation to Enforce Generational Tobacco Ban
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
In News
- The Maldives has become the first country worldwide to impose a historic generational ban on tobacco and vaping.
What is Generational Ban?
- A generational ban on tobacco refers to a progressive legal prohibition designed to create a tobacco-free generation by banning tobacco sales and usage for all individuals born after a specified date.
- Under such a policy, people born beyond that cut-off year are permanently barred from buying, possessing, or using tobacco products throughout their lives, effectively phasing out tobacco use over time.
Status of Tobacco Consumption
- Tobacco-related diseases cause over 7 million deaths annually worldwide, making tobacco one of the leading causes of preventable death globally.
- India is among the largest consumers and producers of tobacco globally.
- Despite global anti-tobacco efforts like the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC), 1.3 billion people still use tobacco products worldwide.
- India implements multiple tobacco control measures like bans on public smoking, pictorial health warnings, advertising restrictions, and the COTPA law.
Source: TH
Encephalomyocarditis Virus (EMCV)
Syllabus: GS2/Health
In News
- Delhi zoo’s lone African elephant died from the rare rodent-borne encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) — the first such case reported in any Indian zoo.
Encephalomyocarditis Virus (EMCV)
- It is a small, non-enveloped single-stranded RNA virus that causes myocarditis, encephalitis, neurological disorders, reproductive issues, and diabetes across various mammalian species.
- Its pathogenesis is both strain- and host-specific, necessitating deeper research into its virulence factors.
- Transmission : Consumption of food and water contaminated with rodent urine or feces
- Ingestion of rats or mice infected with EMCV
- Transplacental (vertical) transmission in swine
- Direct transmission between pigs has not been documented
- Occurrence : EMCV was first identified in 1945 from a gibbon in Florida, with the first pig case reported in Panama in 1958. It is now widespread globally, especially in South America, Australia, China, Europe, Canada, and the US.
Source :IE
National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT)
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- The Supreme Court refused to intervene with an order of the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) which had allowed Aakash Educational Services Ltd, a subsidiary of Byju’s, to proceed with its proposed rights issue.
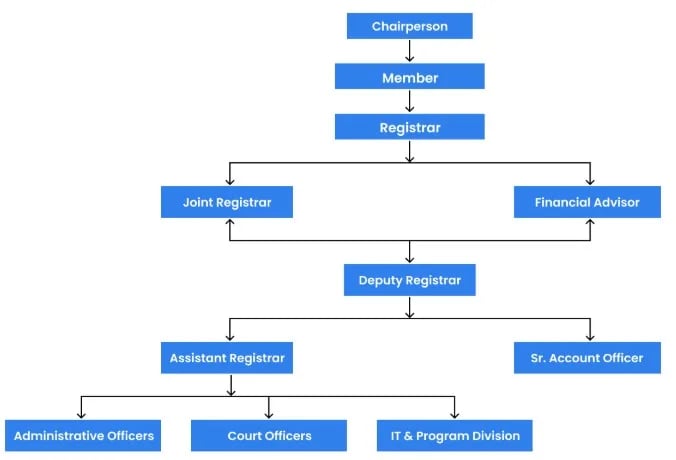
About National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT)
- The National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) was constituted under Section 410 of the Companies Act, 2013, with effect from 2016.
- It functions as a quasi-judicial body to hear appeals against orders of the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) and several other regulatory authorities.
- It also serves as the Appellate Tribunal for hearing appeals against orders passed by the
- National Company Law Tribunal (under Section 61 of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016),
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (under Sections 202 and 211 of the IBC),
- Competition Commission of India (CCI), and
- National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA).
- Organization chart
Source: LIVELAW
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
In News
- The Union Agriculture Minister has ordered on-field investigations into extremely low insurance payouts—some as little as Re 1—under the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, calling them a “mockery” and “injustice” to farmers.
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- It was launched in 2016 to replace the existing National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS) and the Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS).
- It works on the One Nation, One Crop, One Premium.
- Under the scheme, all farmers including sharecroppers and tenant farmers growing “notified crops” in the “notified areas” are eligible for coverage.
- It was initially mandatory for loanee farmers, but was made optional for all in February 2020.
- Coverage: It covers all non-preventable natural risks from pre-sowing to post-harvest, ensuring financial support in the event of crop failure due to natural calamities, pests, or diseases.
- It also covers individual farms nationwide for localized disasters like hailstorms, landslides, floods, and wildfires, as well as post-harvest losses from cyclones, heavy rain, and hail.
- Premium: Premium rates are capped at 2% for kharif crops, 1.5% for rabi crops, and 5% for horticultural crops, with the remaining subsidy initially shared equally by the Centre and states.
- However, the Centre later capped its subsidy at 30% for unirrigated and 25% for irrigated areas. States failing to pay their share on time may be disqualified from implementing the scheme in the next season
Source :IE
Coal India Limited (CIL)
Syllabus: GS3/ Energy and Infrastructure
Context
- Coal India Limited (CIL), is marking the completion of 50 years of its establishment.
About Coal India Limited
- CIL is a Maharatna Public Sector Undertaking under the Ministry of Coal.
- It was established in November 1975.
- Headquarters: Kolkata.
- Products: CIL produces coking coal, semi-coking coal, non-coking coal, washed and beneficiated coal, coal fines, and coke.
- CIL has 21 training Institutes and 76 Vocational Training Centres.
- Strategic Relevance: It contributes to 80% of total domestic coal production and 75% of total coal based generation.
Source: PIB
North Eastern Science & Technology (NEST) Cluster
Syllabus: GS3/Infrastructure
Context
- The Union Minister for Communications and Development of North Eastern Region inaugurated the North Eastern Science & Technology (NEST) Cluster at IIT Guwahati.
About
- NEST Cluster will serve as the nerve centre of the Northeast’s innovation ecosystem, transforming local wisdom into global solutions.
- It will focus on four verticals:
- Grassroots Innovation; Semiconductors & Artificial Intelligence; Bamboo-Based Technologies; Biodegradable Plastics.
- Investment in Assam: Rs 6.2 lakh crore has been invested in the region through the 10% Gross Budgetary Support policy, boosting growth and connectivity.
- Key projects like the Bogibeel Bridge, Bhupen Hazarika Setu, Sela Tunnel, and Jogighopa Multi-Modal Logistics Park have contributed to Assam’s infrastructure development.
- The Act East Policy has also opened new trade routes, cutting travel time between Kolkata and Agartala from 31 hours to just 10 via Bangladesh.
- Projects worth Rs 6,500 crore in Darrang and Rs 18,530 crore across Assam have been launched, showing the Centre’s continued focus on health, education, and industry.
Source: PIB
International Day for Biosphere Reserves
Syllabus: GS3/Environment Conservation
Context
- The International Day for Biosphere Reserves was observed on 3rd November.
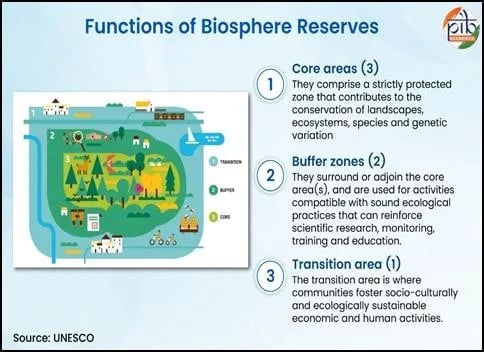
Biosphere Reserves
- Biosphere reserves are areas identified by national governments for conserving biodiversity and promoting sustainable development.
- It includes terrestrial, marine and coastal ecosystems.
- They are nominated by national governments and remain under the sovereign jurisdiction of the states where they are located.
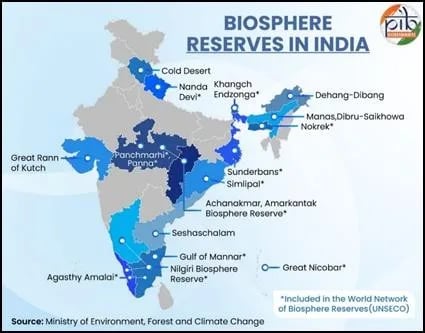
BRs in India
- India has 18 Biosphere Reserves covering 91,425 sq. km, with 13 recognized by UNESCO.
- The programme operates under a Centrally Sponsored Scheme with a 60:40 funding pattern, and 90:10 for North Eastern and Himalayan states.
- In 2025, India’s Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve in Himachal Pradesh was included in UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- National initiatives like Project Tiger, Project Elephant, and Green India Mission complement Biosphere Reserve efforts.
World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR)
- The UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) was formed in 1971.
- It covers internationally designated protected areas, known as biosphere reserves, which are meant to demonstrate a balanced relationship between people and nature.
- They are created under the Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB).
Source: PIB
Torkham Border
Syllabus: GS1/Geography
Context
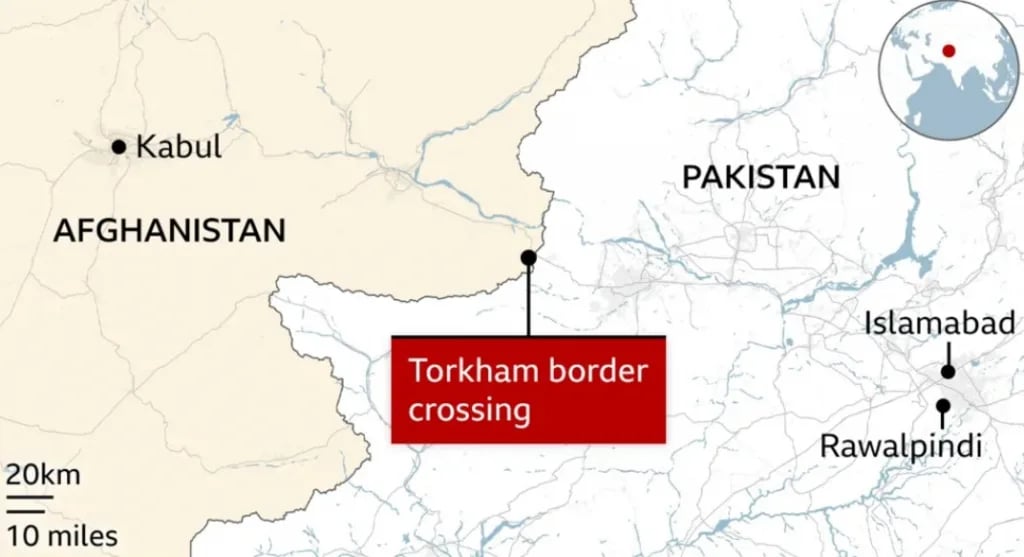
- The Torkham border crossing between Afghanistan and Pakistan has reopened after nearly weeks of closure following deadly border clashes.
About
- The Torkham border is a major crossing point between Afghanistan and Pakistan, located along the Grand Trunk Road on the international border.
- It connects Nangarhar province of Afghanistan with Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan.
- It is the busiest port of entry between the two nations, serving as a key hub for transport, trade, and logistics.
Source: AIR