Genome Sequencing
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- Researchers have sequenced the first whole ancient Egyptian genome from an individual who lived 4,500-4,800 years ago — the oldest DNA sample from Egypt to date.
About
- DNA was successfully extracted from the individual’s teeth.
- The genome of the ancient Egyptian is said to be the most complete and oldest from Ancient Egypt.
Genome
- The genome of an organism is made up of a unique DNA or RNA sequence.
- The human genome is the complete set of genetic information for Homo sapiens.
- It consists of about 3 billion base pairs of DNA, organized into 23 pairs of chromosomes.
- Each chromosome carries a unique set of genes, which are sequences of DNA that encode instructions for building proteins and other molecules essential for life.
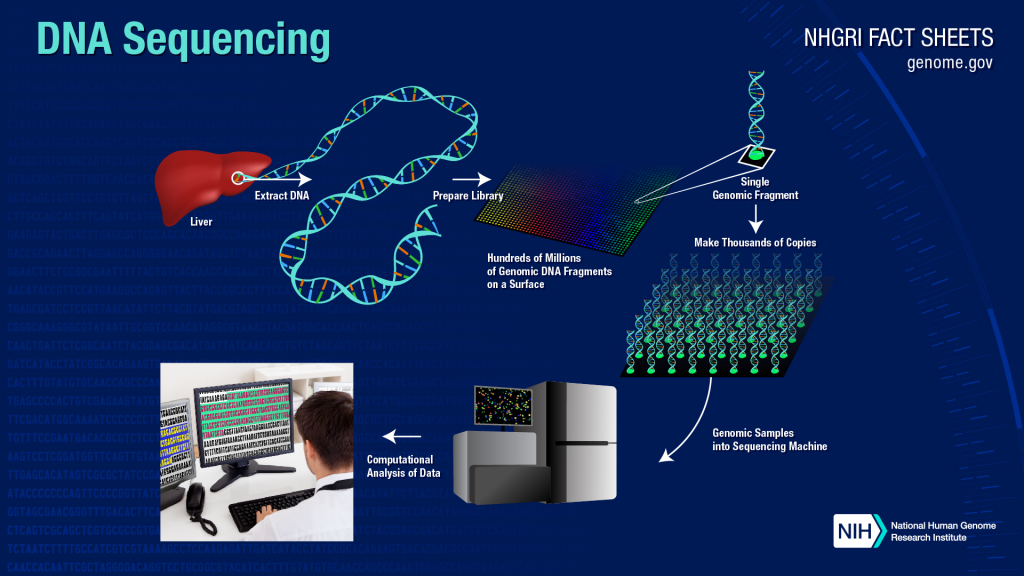
Genome Sequencing
- Each sequence is composed of chemical building blocks known as nucleotide bases.
- Determining the order of bases is called “genomic sequencing” or, simply, “sequencing.”
- The information encoded in the genomes provide researchers with unique genetic “fingerprints.“
- The sequence tells scientists the kind of genetic information that is carried in a particular DNA segment.
Source: TH
DengiAll
Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- India has reached the 50% enrolment mark in its first phase III clinical trial for the indigenous tetravalent dengue vaccine, DengiAll.
About DengiAll
- It is developed by Panacea Biotec Limited under a licensing agreement with the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the primary US federal agency.
- DengiAll has a weakened form of all four dengue virus subtypes and has the same virus composition as the vaccine developed by NIH, except for the inactive ingredients.
- The trial has been approved by the Drug Controller General of India.
- A Phase I and II clinical trial conducted in India revealed a balanced and robust immune response across all four dengue virus types.
- The ICMR-National Institute of Translational Virology (NITVAR) and AIDS Research (formerly ICMR-NARI) is responsible for overall trial coordination.
Dengue
- Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by the Dengue virus (DENV), which has four serotypes (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4).
- It is transmitted primarily by the Aedes aegypti mosquito.
- Spread: The virus does notspread person-to-person directly.
- A mosquito becomes infected by biting a person already infected with the virus, and then can transmit the virus to another person through a subsequent bite.
- Vaccine: Dengvaxia (CYD-TDV) – approved in some countries, recommended for individuals aged 9-16 with a history of dengue infection.
- Dengue fever is one of the top 10 threats to global health, according to the World Health Organisation (WHO).
- Dengue in India: India accounts for a large fraction of global dengue cases; 2.3 lakh cases and 297 deaths were reported in 2024.
Source: IE
C-FLOOD
Syllabus :GS3/Disaster Management
In News
Union Minister of Jal Shakti inaugurated C-FLOOD in New Delhi.
C-FLOOD
- It is a Unified Inundation Forecasting System developed collaboratively by Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) Pune and the Central Water Commission under the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- It is a web-based platform offering two-day advance flood forecasts at the village level through inundation maps and water level predictions.
- It is part of the National Supercomputing Mission and aims to enhance India’s flood management and disaster response capabilities.
Features
- It integrates flood modeling from national and regional agencies, serving as a unified decision-support tool for disaster management.
- Currently, it covers the Mahanadi, Godavari, and Tapi river basins, with plans to include more basins.
- It employs advanced 2-D hydrodynamic modeling to simulate floods.
- Simulations for the Mahanadi Basin run on High Performance Computing at C-DAC Pune under the National Supercomputing Mission, while flood data for the Godavari and Tapi Basins, developed by the National Remote Sensing Centre under the National Hydrology Project, are integrated into the system.
Source :TH
Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI)
Syllabus :GS3/Economy
In News
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has advised all banks to integrate the Financial Fraud Risk Indicator tool .
The Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI)
- It was launched by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) Intelligence Unit in May 2025.
- It is a risk-based metric that classifies a mobile number to have been associated with Medium, High, or Very High risk of financial fraud.
- This classification is an outcome of inputs obtained from various stakeholders including reporting on Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C’s) National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP), DoT’s Chakshu platform, and Intelligence shared by banks and financial institutions
- It helps banks, NBFCs, and UPI providers prioritize actions against high-risk numbers by declining suspicious transactions and issuing alerts.
- Major institutions like PhonePe and ICICI Bank are already using FRI, enhancing fraud prevention in India’s digital payments ecosystem.
Importance
- This technology-driven initiative supports the government’s Digital India vision by strengthening digital trust, enabling real-time fraud detection, and fostering collaboration between telecom and financial sectors.
- This move strengthens the fight against cyber financial frauds through inter-agency collaboration and highlights the importance of API-based real-time data exchange between banks and DoT to improve fraud risk detection.
Source :PIB
SPREE 2025
Syllabus :GS3/Economy
In News
The Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) approved the SPREE 2025 scheme (Scheme for Promotion of Registration of Employers and Employees) during its 196th meeting held in Shimla
The Scheme for Promotion of Registration of Employers and Employees (SPREE) 2025
- It is approved by ESIC and aims to expand social security coverage by allowing unregistered employers and employees—including contractual and temporary workers—to register digitally from July 1 to December 31, 2025, without inspections or demands for past dues.
- Registration will be effective from the declared date, with no contributions or benefits applied retroactively, encouraging voluntary compliance by removing penalties and easing the process.
Importance
- It seeks to bring more establishments and workers under the ESI Act, enhancing access to essential health and social benefits.
- It represents a significant step towards a more inclusive and accessible social security system, supporting ESIC’s goal of universal protection and a welfare-focused labour ecosystem in India.
Source :PIB
NIPCCD renamed as Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development
Syllabus :GS2/Governance
In News
The National Institute of Public Cooperation and Child Development (NIPCCD) has been renamed the Savitribai Phule National Institute of Women and Child Development.
The National Institute of Public Cooperation and Child Development (NIPCCD)
- It was established in 1966 under the Planning Commission and was renamed in 1975 after becoming the apex body for training under the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) program.
- Presently,it is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It is headquartered in Delhi and operates five regional centers across India to address regional needs.
Functions
- It serves as the apex body for training, research, documentation, and capacity building in the field of Women and Child Development.
- It plays a pivotal role in strengthening implementation mechanisms under various flagship schemes through its online and physical training programmes .
Source :PIB