.jpg)
In News: The Saudi-led coalition said it intercepted a Houthi ballistic missile targeting the kingdom, including the southern cities of Khamis Mushait and Jizan.
- The Iran-backed Houthis have escalated attacks on the kingdom to get control from the Saudi-backed Yemeni government.
- The assaults came as Saudi Arabia hosted a Formula E championship on the outskirts of Riyadh, which state media said was attended by de facto ruler Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman.
(Image Courtesy: BBC)
Key Points
- Yemen Crisis –
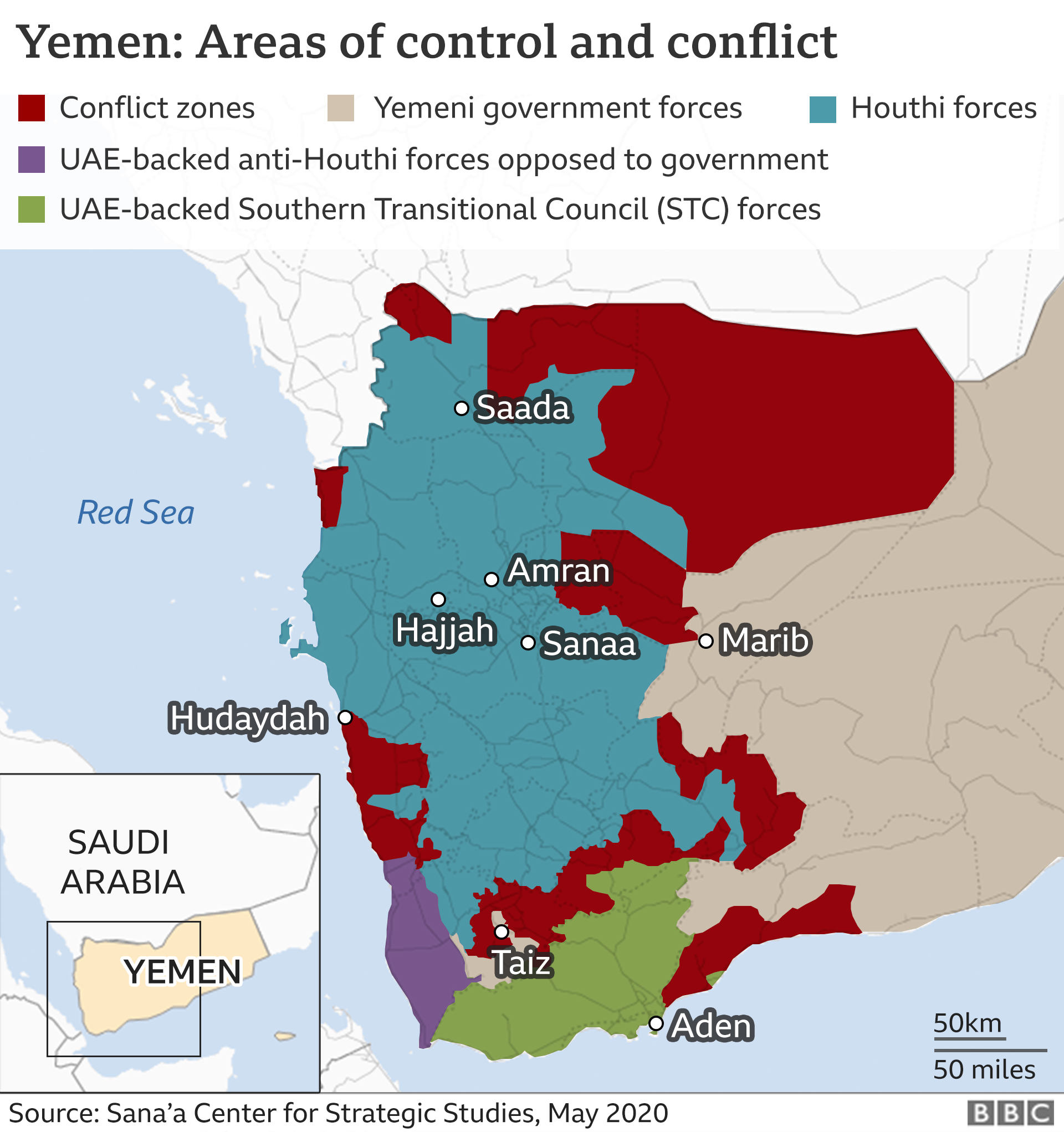
- Since April 2015, Yemen has been in the grip of a war where the Saudi-led coalition and the internationally recognised government are battling with the Houthis to control key ports and cities in the country.
- The conflict is also seen as part of a regional power struggle between Shia-ruled Iran and Sunni-ruled Saudi Arabia.
- Houthis-
- The Houthis, officially known as Ansar Allah (Partisans of God), are an Iranian-backed, Shiite Muslim military and political movement in Yemen.
- Its members, who subscribe to the minority Zaidi sect of Shiite Islam, advocate regional autonomy for Zaidis in northern Yemen.
- They fought a series of rebellions against Saleh during the previous decade, and took advantage of the new president’s weakness by taking control of their northern heartland of Saada province and neighbouring areas.
- The intervention of the Saudi-led coalition
- The Saudi-led coalition intervened in Yemen in March 2015 after the Houthis ousted the internationally recognised government from power in the capital, Sanaa.
- The coalition received logistical and intelligence support from the US, UK and France.
- Houthis response –
- The Houthis have not been dislodged from Sanaa and north-western Yemen.
- They have been able to maintain a siege of the third city of Taiz and to launch regular ballistic missile and drone attacks on Saudi Arabia.
- In September 2019, Saudi Arabia’s eastern oil fields of Abqaiq and Khurais were attacked by air, disrupting nearly half the kingdom’s oil production – representing around 5% of global oil output.
- Ceasefire
- After six months of fighting, the warring parties agreed on a ceasefire at talks in Sweden.
- The Stockholm agreement required them to redeploy their forces from Hudaydah, establish a prisoner exchange mechanism, and to address the situation in Taiz.
- The UN hoped the agreement would clear the way for a political settlement to end the civil war, but in January 2020 there was a sudden escalation in hostilities between the Houthis and coalition-led forces, with fighting on several front lines, missile strikes and air raids.
- After six months of fighting, the warring parties agreed on a ceasefire at talks in Sweden.
- Saudi Arabia announced a unilateral ceasefire in April 2020 due to a coronavirus pandemic but the Houthis rejected it, demanding the lifting of air and sea blockades in Sanaa and Hudaydah.
- Implications on
- World
- It can greatly exacerbate regional tensions.
- It also worries the West because of the threat of attacks – such as from al-Qaeda or IS affiliates – emanating from the country as it becomes more unstable.
- Yemen is also strategically important because it sits on a strait linking the Red Sea with the Gulf of Aden, through which much of the world’s oil shipments pass.
- World
India –
- One of India’s most important shipping routes passes through the Gulf of Aden, accounting for imports of $50 billion and exports of $60 billion every year.
- Indian nationals, including Hindus, Muslims and Parsis, have lived in Aden since the mid-1880s.
- 8 million expats living in the region with more than $80 billion of incoming remittance annually.
- Therefore the crisis in Yemen can affect the remittances and destroy the shipping routes.
Previous article
Formation & Promotion of 10,000 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs)
Next article
Cyber Warfare