Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The Minister of Commerce and Industry has said that in 20-25 years from now India will be a $30 trillion economy.
About
- GDP: The size of an economy refers to the annual gross domestic product or GDP.
- The GDP is the total market value of all goods and services produced within a country.
- In the 2024 financial year India’s GDP was $3.9 trillion.
- Calculation of GDP: In a global context, a country’s GDP is stated in US dollar terms so that all economies can be compared easily.
- The GDP calculated is nominal GDP — not the real GDP in which the effect of inflation is negated).
- The projection of GDP requires two things: The projection of India’s nominal GDP in rupee terms as well as the projection of rupee-dollar exchange rate.
- Both matter because if the 2024 exchange rate had remained at ₹65 per dollar (as in 2014), India’s ₹330 trillion GDP would equal $5 trillion. But with the rate at ₹84 per dollar, it amounts to only $3.9 trillion.
Projected Growth
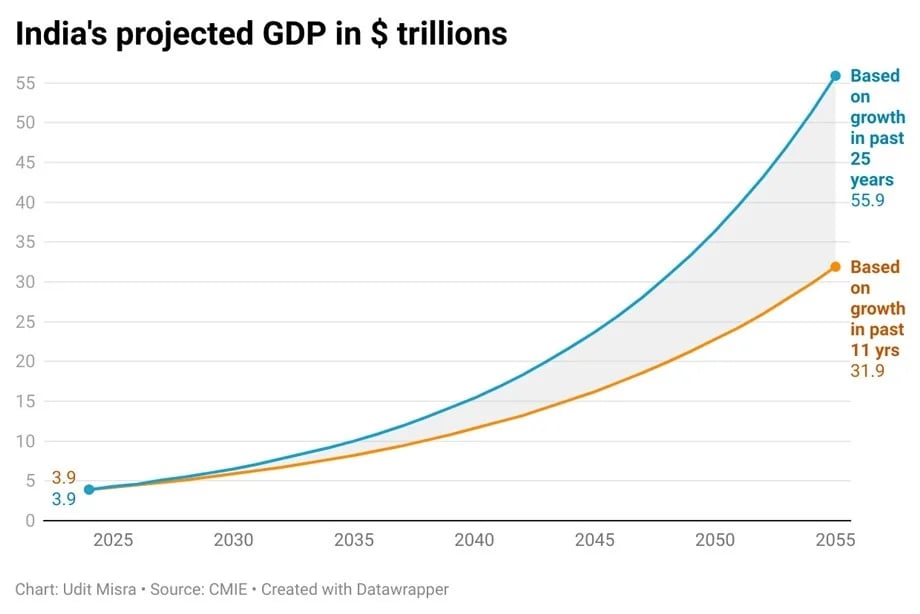
- Data reveals that India’s nominal GDP has registered a CAGR (compounded annual growth rate) of 11.9% since the financial year 2000.
- Further, the Indian rupee has depreciated against the dollar at a CAGR of 2.7% since 2000.
- So, if one presumes that India’s growth will be exactly the same and the rupee will depreciate exactly in the same manner over the coming 25 years, then India’s GDP will cross $30 trillion in 2048.
Challenges
- Slowing Growth Momentum: Nominal GDP growth has fallen from 11.9% (2000–2014) to 10.3% (2014–2024), reflecting weaker economic momentum.
- Rupee Depreciation: Faster depreciation (3.08% CAGR since 2014) reduces India’s GDP value in dollar terms even if rupee GDP grows steadily.
- Export Competitiveness: Limited diversification and reliance on a few sectors reduce India’s ability to sustain export-led growth.
- Infrastructure Deficits: Logistics, power, and urban infrastructure gaps increase costs and limit industrial expansion.
- Human Capital Challenges: Skill mismatch, low female labour participation, and underinvestment in health and education reduce labour productivity.
- Fiscal and Financial Pressures: High fiscal deficits and rising debt constrain public investment capacity.
- Global Economic Headwinds: Geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and protectionist trends could affect trade and capital flows.
Government Initiatives
- Make in India (2014): Promotes domestic manufacturing and aims to raise the manufacturing share in GDP to 25%.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes: Encourage large-scale manufacturing across 14 sectors to boost exports and job creation.
- National Industrial Corridor Programme: Develops modern industrial infrastructure and connectivity.
- PM Gati Shakti (2021): A National Master Plan for multi-modal connectivity integrating roads, railways, ports, and logistics.
- Bharatmala and Sagarmala: Enhance road and port connectivity to reduce logistics costs.
- Skill India Mission: Enhances workforce capabilities through vocational training.
- Start-Up India & Stand-Up India: Fosters entrepreneurship and innovation.
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and negotiations: With the UK, EU, UAE, etc., to expand export markets.
- ‘Act East’ and ‘Indo-Pacific’ strategies: Strengthen economic and strategic integration with Asia-Pacific.
Way Ahead
- Growth momentum has weakened in the last decade, small variations in growth or exchange rates can cause large long-term effects.
- As economies expand, growth rates naturally moderate, but India is still too small compared to the US and China to afford such moderation.
- To make the $30 trillion projection credible, India must sustain and accelerate its growth rate.
Source: IE
Previous article
Joint Leaders’ Declaration: APEC Summit in South Korea
Next article
Rising Energy Demand of AI Data Centres