Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
Context
- The Union Government announced two cross-border railway projects which will connect Bhutan with the bordering areas of Assam and West Bengal.
Background
- The genesis of these two projects lies in the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between Bhutan and India in 2005.
- Why Gelephu and Samtse?
- Gelephu and Samtse are the major export-import hubs in Bhutan and serve the 700-km long India-Bhutan border.
- Gelephu is being developed as “Mindfulness City” and Samtse is being developed as an industrial town by the Government of Bhutan.
About the Rail Projects
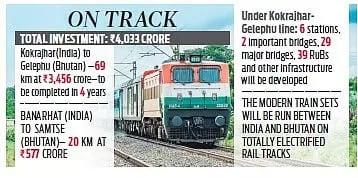
- Kokrajhar–Gelephu Line: It will connect Sarpang district in Bhutan with Kokrajhar and Chirang districts in Assam.
- It is declared a Special Railway Project for fast-track approvals and land acquisition.
- It will span 69 km and is estimated to cost Rs 3,456 crore.
- Banarhat–Samtse Line: It will connect Samtse district in Bhutan with Jalpaiguri district in West Bengal.
- The line will cover 20 km and is estimated to cost Rs 577 crore.
Significance of the Project
- Strengthening ties with Bhutan:
- Development assistance: This initiative builds on India’s long-standing role as Bhutan’s largest developmental partner and its recent commitment of approximately $1.2 billion for Bhutan’s 13th Five-Year Plan.
- Enhanced contact: Facilitating smoother passenger and cargo movement is expected to boost people-to-people connections and cultural exchanges.
- Increasing trade:
- Seamless connectivity: For landlocked Bhutan, the railway links will provide seamless access to Indian ports and markets, significantly lowering freight costs for its exports.
- Bolstering key hubs: The new lines will support the economic development of Gelephu as a new commercial hub and Samtse as an industrial center.
- Free trade access: As Bhutan’s top trading partner, the projects will further enhance the benefits of the 2016 free trade agreement between the two nations.
- Counterbalancing China’s influence: The railway lines are located near the sensitive Siliguri Corridor (Chicken’s Neck Area), a narrow strip of land linking mainland India to its northeastern states.
- By improving security and supply chains in this region, the project helps mitigate potential security risks in the wake of China’s growing regional footprint.
What are the challenges?
- Land Acquisition and Terrain: Southern Bhutan and northeast India have hilly and forested terrain, making land acquisition complex and time-consuming.
- Negotiating with local communities and obtaining environmental clearances could cause delays.
- Construction and Engineering: Projects require numerous bridges, viaducts, and underpasses in challenging topography.
- There are risks of geological hazards such as landslides, river floods, and seismic activity.
- Strategic and Geopolitical Risks: Proximity to the China–Bhutan–India border requires infrastructure security and strategic considerations.
Way Ahead
- The railway projects mark a historic milestone in India–Bhutan relations, establishing the Himalayan nation’s first-ever train links.
- With careful implementation and bilateral cooperation, the project poised to become a transformative infrastructure initiative, benefiting both nations and the broader eastern Himalayan region.
Source: IE
Previous article
100 Years of UPSC : the guardian of meritocracy
Next article
News In Short – 1 October, 2025