Hul Diwas
Syllabus: GS1/History and Culture
Context
- June 30 is observed as Hul Diwas, marking the anniversary of the 1855 Santhal rebellion/ Santhal Hul, one of the earliest peasant uprisings against the British.
Santhal Hul
- Santhal Hul of 1855 was a revolt against imperialism led by four brothers, Sidho, Kanho, Chand, and Bhairav Murmu, along with sisters Phulo and Jhano.
- The Santhals also fought against the upper castes, zamindars, darogas, and moneylenders, described by the umbrella term ‘diku’.
- Significance: The rebellion led to the enactment of the Santhal Parganas Tenancy Act of 1876 and the Chotanagpur Tenancy Act of 1908, which aimed to safeguard tribal land rights and cultural autonomy.
Genesis of the uprising
- In 1832, the British demarcated a region in present-day Jharkhand, called Damin-i-Koh, as a settlement area for the Santhal tribe.
- While initially intended for peaceful settlement and agricultural development, the region eventually experienced exploitation by outsiders (dikus), leading to land alienation among the Santhals.
- The Murmu brothers led around 60,000 Santhals against the East India Company and engaged in guerrilla warfare.
- The British hanged Sidhu in 1855, followed by Kanhu in 1856.
Source: AIR
MY Bharat 2.0 Platform
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
In News
- The Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports (MYAS) signed an MoU with the Digital India Corporation (DIC) to develop MY Bharat 2.0 Platform.
MY Bharat
- It is a dynamic technology platform that serves as an institutional framework to engage and mobilize the youth of India in a structured and meaningful manner.
- It encourages purposeful youth engagement and civic responsibility by allowing young citizens to create digital profiles, participate in volunteering and learning programs, connect with mentors and peers, and contribute to building a developed India by 2047.
- It was officially launched in 2023 and as of now, over 1.76 crore youth and more than 1.19 lakh organizations have registered on MY Bharat platform.
- MY Bharat 2.0 Platform is an upgraded national youth platform aimed at digitally empowering and connecting India’s youth.
- It will be rebuilt with modular architecture for scalability, include new AI-driven features like a Smart CV Builder, personalized digital profiles, AI chatbots, speech-to-text, and WhatsApp integration, and offer enhanced accessibility through voice navigation.
Source: PIB
Civil Registration System (CRS) and Sample Registration System (SRS)
Syllabus: GS2/Governance
Context
- The Civil Registration System (CRS) reports of the past two decades show that Bihar has been lagging far behind the rest of the country in registering births.
Civil Registration System (CRS)
- Civil Registration System (CRS), popularly known as birth and death registration system, is the recording of vital events i.e. Birth, Death & Still Birth under the statutory provisions on a continuous and permanent basis.
- CRS falls under the Concurrent list of the Constitution.
- Governed by: The Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969.
- Administered by: The Office of the Registrar General of India (RGI) under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Vital statistics generated from civil registration significantly contribute to the formulation of effective and efficient evidence-based policy across multiple sectors.
Sample Registration System (SRS)
- In order to unify the Civil Registration activities, the Registration of Births & Deaths Act, 1969 was enacted.
- With a view to generate reliable and continuous data on these indicators, the Office of Registrar General, India, initiated the scheme of sample registration of births and deaths in India popularly known as Sample Registration System (SRS) in 1964-65 on a pilot basis and on full scale from 1969-70.
- The SRS since then has been providing data on a regular basis.
Source: TH
Kombucha
Syllabus: GS2/Health
In News
- A recent 8-week study in Brazil found that Kombucha improves gut bacteria—especially in people with obesity—by increasing beneficial microbes and reducing harmful ones, though it didn’t improve blood sugar or inflammation markers.
Kombucha
- It is a fermented tea and it is one of the few drinks that offers complexity and texture without being high in sugar or caffeine.
- It originated in northeast China around 220BCE and was valued for its invigorating and detoxifying effects.
- Kombucha is gaining popularity in India, with the market growing from $45 million in 2020 to $102 million in 2024.
- Kombucha is promoted for digestive, immune, and metabolic benefits, but human evidence is limited.
Source:TH
India Reiterated Its Commitment to the Global South
Syllabus: GS2/IR
In News
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s, 5-nation tour is significant for India’s outreach to the Global South.
Global South
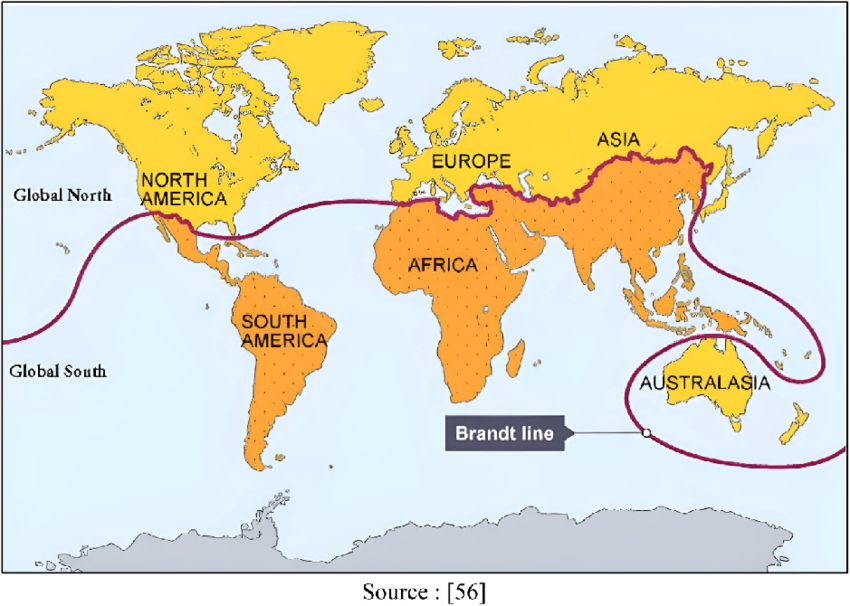
- Definition: The Global South refers to countries that are economically and socially less developed, primarily located in Asia, Africa, Latin America, and Oceania.
- Although named ‘South’, not all Global South countries lie in the Southern Hemisphere (e.g. India and China are in the Northern Hemisphere).
- Origin of the Term: Coined during the Cold War era, it gained popularity after the Brandt Report (1980), which highlighted global inequalities using a conceptual line known as the Brandt Line.
- Characteristics: Many of these countries face severe challenges such as poverty, food crises, weak health infrastructure, debt, terrorism, and conflict.
- Most of the world’s least developed countries belong to this group and require global support and fair treatment to achieve sustainable growth.
- The Global South seeks a stronger collective voice to ensure equitable participation in global policymaking, especially on trade, intellectual property, health, and food security.
India’s Role
- India has long been a key leader advocating for the Global South, drawing on its democratic values and shared development goals with other developing nations.
- India played a pivotal role in founding major movements representing developing countries, including the 1955 Bandung Conference, the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) in 1961, and the Group of 77 (G-77) in 1964.
- These platforms aimed to promote equality, self-determination, multilateralism, and South-South cooperation.
- In recent years, India has actively strengthened engagement with the Global South through initiatives like the annual ‘Voice of Global South Summit,’ with the third edition held in August 2024, gathering leaders from over 120 countries.
- These efforts align with India’s vision of inclusive growth and global cooperation under the philosophy of “One Earth, One Family, One Future.”
Source :IE
Sea Ship Observer Mission
Syllabus: GS2/Regional Groupings
Context
- The Coast Guards of India, Japan, United States, and Australia have launched the first-ever ‘QUAD at Sea Ship Observer Mission.’
About
- The observer-at-sea engagement marks a first-of-its-kind initiative among the Indian Coast Guard, Japan Coast Guard, United States Coast Guard, and Australian Border Force.
- It is based on the Wilmington Declaration adopted at the QUAD Leaders’ Summit in 2024.
- The mission reflects the collective resolve of the QUAD to strengthen a free, open, inclusive and rules-based Indo-Pacific.
- India’s involvement underlines its strategic SAGAR (Security and Growth for All in the Region) doctrine and supports its broader Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
Source: TH
Altermagnets
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- Scientists at the S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences have discovered an exceptional property in a newly identified magnetic material—Chromium Antimonide (CrSb).
- This material has become the world’s first known altermagnet to exhibit direction-dependent conduction polarity (DDCP) acting as both p-type and n-type conductor within a single crystal, based purely on direction.
What are Altermagnets?
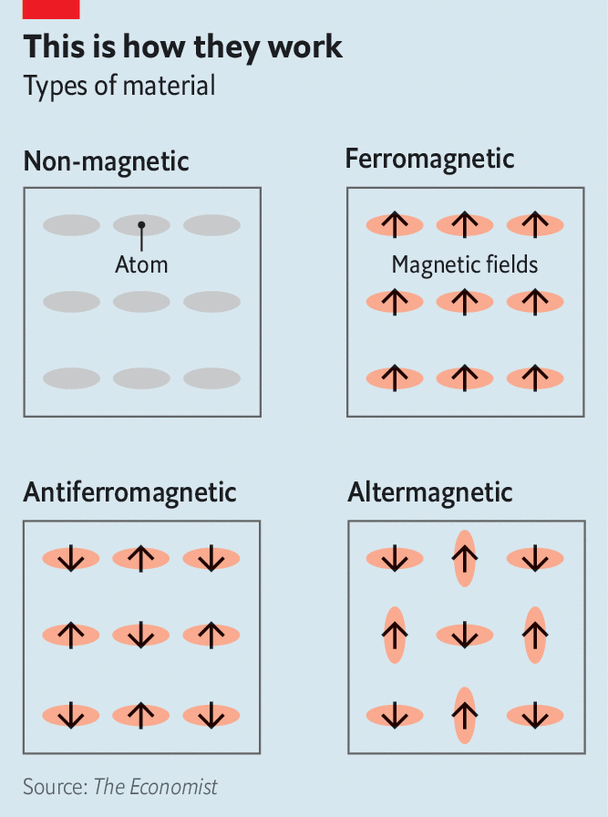
- Altermagnets represent a novel class of magnetic materials that uniquely combine the internal spin ordering characteristic of anti-ferromagnets with the functional advantages associated with ferromagnets.
- Despite this internal magnetic order, they exhibit zero net external magnetization.
- Their “hidden” magnetic symmetry allows for unprecedented control over electron spin and transport properties without producing any external magnetic signatures.
Source: PIB
Botrytis Cinerea
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- A recent study has revealed that Botrytis cinerea cannot be cloned, as no single nucleus within its cells contains a complete set of chromosomes.
- Instead, its genetic material is distributed across multiple nuclei—a finding that challenges traditional principles of cell biology.
About
- Botrytis cinerea, commonly known as noble rot, is a necrotrophic fungus that infects over 200 plant species.
- It is most famously used in wine-making, where it infects grapes, dries them, and concentrates their sugars—producing high-quality sweet wines such as Sauternes (France) and Tokaji Aszú (Hungary).
- While beneficial under controlled conditions, it is a major plant pathogen in agriculture, causing grey mould disease in crops like strawberries, tomatoes, and lettuce.
Concerns of Botrytis Cinerea
- The fungus thrives in humid, cool environments and spreads rapidly, especially in greenhouses.
- It produces spores (conidia) that are easily carried by wind, water, or insects.
- It has developed resistance to multiple fungicides, making disease control difficult and increasing crop losses.
Source: TH
India Energy Stack
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance, GS3/Infrastructure, Energy,
Context
- The Ministry of Power has set up a 17-member task force, mentored by Nandan Nilekani, to design the India Energy Stack – a unified digital public infrastructure (DPI) for the power sector.
What is the India Energy Stack?
- India Energy Stack is a digital framework to integrate India’s fragmented energy ecosystem.
- It enables real-time coordination between producers, consumers, grid operators, regulators, and energy fintech.
- It supports peer-to-peer energy trading, decentralisation, carbon tracking, and data-driven decision-making.
- It aims to make the energy sector interoperable, scalable, and transparent.
Need for a Unified Digital Framework in the Power Sector
- India’s energy sector is fragmented due to its concurrent governance structure . This leads to;
- No unique IDs for consumers/assets/stakeholders.
- Lack of harmonised, real-time data.
- Incompatibility between platforms, hindering scalability.
- No interoperability, restricting cross-DISCOM and regional integration.
Source: IE
Akash Air Defence System
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
In News
- Brazil has expressed interest in purchasing India’s Akash Air Defence System, a significant development ahead of the 17th BRICS Summit.
About Akash Air Defence System
- Akash is a medium-range, mobile surface-to-air missile (SAM) system.
- Its primary purpose is to neutralize aerial threats like enemy aircraft, drones, and missiles in both defensive and offensive operations, protecting critical points and areas.
- The Akash system is a product of the “Make in India” initiative, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) and Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- Its objective is to strengthen India’s layered air defense by bridging the gap between short and long-range interceptors.
- It has a range of 4.5 km to 25 km, altitude coverage of 100 m to 20 km, & it can travel with supersonic speed (Mach 1.8 to 2.5).
Source: TH
GOSAT-GW Satellite
Syllabus: GS3/Space
Context
- Japan has successfully launched its GOSAT-GW satellite aboard the H-2A rocket as part of Tokyo’s ongoing efforts to monitor and mitigate climate change.
About the Satellite
- The GOSAT-GW, or Global Observing Satellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle, is a third series in the mission to monitor carbon, methane and other greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere.
- Within one year, it will start distributing data such as sea surface temperature and precipitation with much higher resolution to users around the world, including the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Do you know?
- This launch marked the 50th and final flight for Japan’s trusted H-2A rocket, which has been operational since 2001 with a near-perfect success rate.
- The H-2A will now be fully replaced by the next-generation H3 rocket, designed to be more cost-competitive and capable of carrying larger payloads to strengthen Japan’s position in the global satellite launch market.
Source: TH
Previous article
MNRE Revises Biomass Guidelines to Boost Bio Energy
Next article
National Sports Policy (NSP) 2025