Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The RBI Handbook of Statistics on Indian States 2024–25 reveals that export growth is increasingly concentrated in a few developed coastal and industrial States, masking deep regional and employment-related challenges.
Pattern in India’s Exports
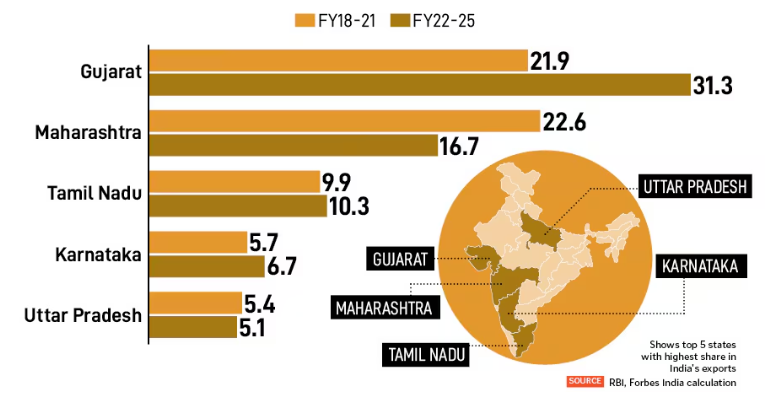
- Rising dominance of few States: The top 10 States now account for over 91 percent of India’s exports in FY25, up from 84 percent in FY22.
- The top five States, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Uttar Pradesh, together contribute nearly 70 percent of national exports.
- Regional divergence: Coastal western and southern States are integrating deeper into global supply chains.
- Large parts of northern and eastern India are gradually decoupling from the trade engine.
Reasons Behind Export Concentration
- Infrastructure advantages: Coastal States benefit from ports, industrial corridors, multimodal logistics and proximity to global markets.
- Agglomeration economies: Established industrial ecosystems attract capital, skilled labour, suppliers and ancillary industries, reinforcing dominance.
- Shift from cost to complexity: Global capital increasingly favours regions with high economic complexity, diversified export baskets and strong institutional capacity.
- Global trade constraints: WTO data shows global merchandise trade growth slowing to 0.5–3 percent, while UNCTAD estimates suggest the top 10 exporters control around 55 percent of global trade.
- This intensifies competition and favours already-integrated regions.
- Financial depth asymmetry: High-export States like Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh record Credit–Deposit ratios above 90 percent, enabling local savings to fund local industry.
Impact of Export Concentration
- Regional inequality: Coastal western and southern States integrate deeper into global trade, while northern and eastern regions decouple.
- Fragile export resilience: Over-reliance on a few States and sectors heightens vulnerability to regional or sector-specific shocks.
- Limited job creation: Export growth no longer guarantees mass employment, weakening its role as a development lever.
- Fiscal and social stress: Persistent regional divergence strains cooperative federalism and inclusive growth objectives.
Government Initiatives to Improve Hinterland Export Competitiveness
- Districts as Export Hubs (DEH): It aims to transform each district into an export hub by focusing on infrastructure development (processing, testing, logistics) and capacity building of local producers.
- It is integrated with One District One Product (ODOP) for decentralised and balanced export promotion.
- Export Promotion Mission (EPM) is India’s new, unified six-year program (FY 2025-2031) to explicitly prioritises;
- Non-traditional districts and landlocked States.
- Labour-intensive and MSME-driven exports.
- Agriculture Export Policy & APEDA Financial Assistance Scheme (FAS) targets agricultural and processed food exports from rural and inland areas.
- Towns of Export Excellence (TEE): Identifies towns with sector-specific export potential (handicrafts, handlooms, textiles, leather). It provides financial assistance, technical upgradation, skill development, and export marketing support.
- PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan & National Logistics Policy (NLP): It aims to reduce India’s logistics cost and improve trade efficiency. It benefits for hinterland regions with
- Improved road, rail, inland waterway, and multimodal connectivity.
- Development of dry ports, logistics parks and freight corridors.
- Faster movement of goods from production centres to ports.
Way Ahead
- Strengthen district-level institutions, logistics, finance, and skill ecosystems to enable hinterland regions to enter medium- and high-complexity export value chains.
- Complement export growth targets with metrics on employment generation, regional dispersion, and value-chain integration to ensure inclusive and balanced trade-led development.
Source: TH
Previous article
National Consumer Day
Next article
News In Short 24-12-2025