Syllabus: GS1/Society; GS2/Governance
Context
- National Girl Child Day is celebrated annually on January 24.
About
- National Girl Child Day has been observed annually on January 24 since 2008.
- Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development (MWCD).
- It promotes awareness of girls’ rights, empowerment, and equal opportunities in India.
Challenges Faced by India in ensuring Girls’ Rights
- Cultural Preference for Sons: Sons were preferred for carrying on the family name, performing religious rites, and providing financial support in old age.
- This led to a neglect of daughters, who were seen as a financial burden due to dowry practices.
- Gender Discrimination: Girls have historically faced neglect in terms of nutrition, education, and healthcare, which contributed to higher mortality rates among females.
- Female Infanticide: In some regions, female infants were either abandoned or killed due to their perceived lower value.
- Sex-Selective Abortion: Advances in medical technology, such as ultrasound, enabled the practice of sex-selective abortion, leading to a disproportionate number of male births.
- Economic Factors: In agrarian societies, the labor of sons was seen as more valuable for agricultural work, further reinforcing the preference for male children.
- Lack of Access to Education: Limited access to quality education, especially in rural areas, affecting girls’ future opportunities.
- Safety and Security: High rates of gender-based violence, including sexual harassment, domestic violence, and trafficking.
- Child Marriage: Prevalence of child marriage, particularly in rural areas, which affects women’s health, education, and autonomy.
- Social Norms and Expectations: Rigid societal roles that limit women’s freedom and opportunities for self-expression and growth.
Government Initiatives
Achievements
- Improved Sex Ratio: Significant progress has been made through sustained efforts, particularly under the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) scheme, with the Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB) rising from around 918 in 2014-15 to 930 in 2023-24 at the national level.
- Progress in School Education for the Girl Child: For the period 2024-2025, the Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) of girls at the secondary level has reached 80.2%, as per UDISE report.
- 97.5 per cent of schools nationwide are equipped with girls’ toilet facilities.
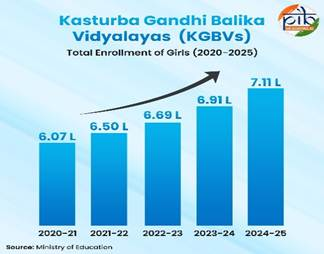
- Prevention of Child Marriage: As of January 2026, a total of 2,153 child marriages have been prevented, and 60,262 Child Marriage Prohibition Officers have been appointed across the country.
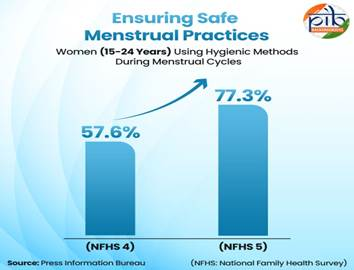
- Menstruation Care:
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY): By 2024, more than 4.2 crore accounts had been opened nationwide, indicating strong public participation and confidence in the scheme.
Way Ahead
- Community Awareness and Education: Campaigns like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao should continue to raise awareness about the value of the girl child and the harmful effects of gender discrimination.
- Improving Women’s Health and Access to Healthcare: Providing better healthcare access for women and girls, especially in rural areas, can help reduce female mortality rates.
- Changing Social Norms and Attitudes: Promoting gender-sensitive education, involving men in gender equality discussions, and tackling the dowry system can help break the traditional biases against girls.
- Robust Data Collection and Research: Continuous monitoring and research into the reasons behind sex ratio imbalances can help tailor future interventions and track the success of existing initiatives.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Facts In News 23-01-2026
Next article
71 Fugitives Located Abroad in 2024-25