Sangai Festival
Syllabus: GS1/Art and Culture
In News
- The Sangai Festival in Manipur opened amid protests by internally displaced persons and NGOs, who argued that the government should address the ongoing Kuki-Zo–Meitei ethnic conflict before holding tourism events.
Sangai Festival
- It is a grand celebration of Manipur’s rich tradition and culture held annually from 21–30 November in Manipur since 2010.
- It is named after the rare Sangai deer.
- The festival showcases a wide range of activities including Manipuri arts and classical dance forms such as Ras Leela, folk dances like the Kabui Naga dance and Bamboo dance, indigenous martial arts including Thang-Ta, and traditional sports like Yubi Lakpi and Sagol Kangjei (modern polo).
Source :TH
Mount Semeru
Syllabus: GS1/ Physical Geography
In News
- Mount Semeru, located in eastern Java (Indonesia), erupted recently.
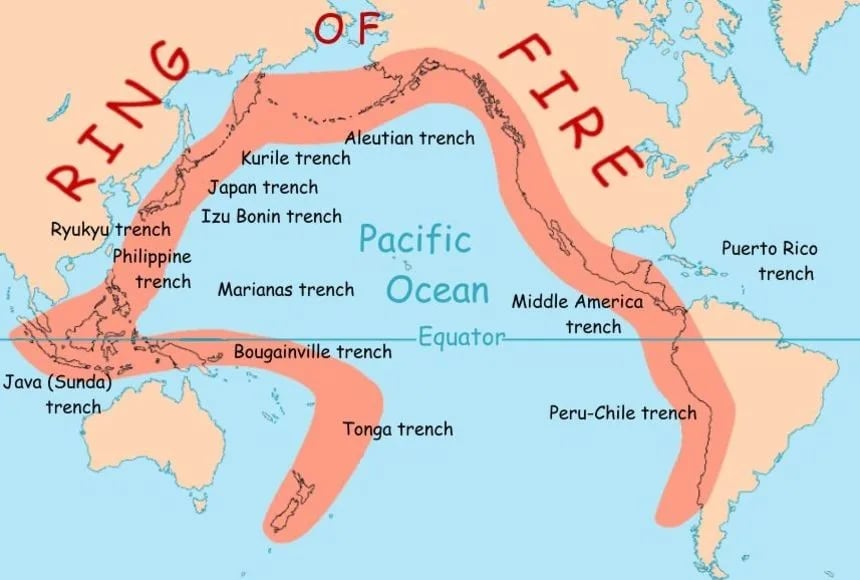
Why is Indonesia Prone to Volcanic Eruptions?
- Indonesia sits on the convergent boundary where the Indo-Australian Plate subducts under the Eurasian Plate
- This process forms a chain of stratovolcanoes across Java, Sumatra, and the Sunda Arc.
- It lies at the heart of the Ring of Fire, which accounts for 75% of the world’s volcanoes and 90% of earthquakes.
Source: TH
Geological Survey of India (GSI)
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
In News
- The International Seminar titled “Unearthing the Past, Shaping the Future: 175 Years of GSI” was inaugurated by the Union Minister of Coal & Mines as part of the Geological Survey of India’s (GSI) 175th Foundation Year celebrations.
About Geological Survey of India
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is India’s premier national geoscientific organization under the Ministry of Mines, established formally in 1851 by Sir Thomas Oldham.
- Historically, geological work in India began in the early 1800s with surveys by the Survey of India and army officers.
- The term “Geological Survey of India” was first used in 1848 during coal investigations led by John McClelland.
- Under Oldham’s leadership, GSI expanded its focus beyond coal to systematic geological mapping of India’s surface and subsurface rock formations, employing techniques such as fossil index identification before radiometric dating was available.
Key Functions
- Geological Mapping and Surveys: Comprehensive mapping of surface and subsurface geology, including ground, airborne, and marine surveys.
- Mineral Exploration: Scientific exploration and assessment of mineral, energy (including coal, oil), and water resources.
- Geohazard Studies: Conducting seismotectonic research, glaciology, climate-related geostudies, and hazard risk analysis.
- Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Studies: Supporting infrastructure planning, groundwater studies, land stability analysis, and environmental assessments.
Source: PIB
Protected Area Permit
Syllabus: GS2/ Polity
In News
- Nagaland Chief Minister has urged the Union Home Minister to urgently review the re-imposition of the Protected Area Permit (PAP) regime in the state.
About Protected Area Permit (PAP)
- Overview: The Protected Area Permit (PAP) is a special permit required by foreign nationals to visit certain sensitive regions of India that lie close to international borders.
- This system is mandated under the Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958.
- Eligibility: PAP is mandatory for foreign citizens (excluding Bhutanese nationals) to enter these areas. Indian citizens require an Inner Line Permit (ILP) for some overlapping regions.
- Permits are usually granted for specific tourist circuits/routes and are time-bound; overstaying is prohibited.
- Generally, only group tourists (minimum of two persons) traveling with registered tour operators are allowed.
- States/Areas Under PAP (2025 Update): Whole of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mizoram, & Nagaland.
- Parts of Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, and Rajasthan.
- Validity and Compliance: PAP is valid only for the specified area, route, and time mentioned in the permit.
- Difference from Restricted Area Permit (RAP): The RAP regime applies mainly to the Andaman & Nicobar Islands and parts of Sikkim; policies are similar but locations are different.
Source: AIR
Integrated Child Development Services Programme
Syllabus: GS2/Welfare Scheme
In News
- Integrated Child Development Services programme has expanded widely and improved nutrition, education, and early childhood care through anganwadis.
Integrated Child Development Services programme
- Overview: Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) is India’s flagship early childhood care and development programme, providing a package of nutrition, health and pre-school education services to children under 6 years and their mothers through a nationwide network of Anganwadi centres.
- ICDS is a centrally sponsored scheme launched on 2 October 1975 in line with the National Policy for Children and is today one of the world’s largest community‑based child development programmes.
- Over time, ICDS has been restructured as Anganwadi Services and is now subsumed under the Saksham Anganwadi and POSHAN 2.0 umbrella to integrate nutrition and early childhood care.
Source :TH
Amoebic Meningoencephalitis
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
In News
- Karnataka has issued guidelines for Sabarimala pilgrims following cases of amoebic meningoencephalitis or brain fever.
About
- The “brain-eating amoeba” refers to Naegleria fowleri, a free-living, thermophilic amoeba found in warm freshwater.
- It causes a rare but almost always fatal infection called Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM).
- It enters the human body typically through the nose, often during activities such as swimming, diving, or water sports in contaminated water.
- It travels via the olfactory nerve to the brain and destroys brain tissue.
- It cannot infect through drinking water and cannot spread person-to-person.
Source: IE
Meerut Bugle
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- Bugle, an instrument common with the drills of armed forces and used in wars, ceremonies, and parades for decades, has earned a GI tag.
About Meerut Bugle
- Meerut’s association with bugle-making dates back to the late 19th century. The instrument’s journey has been parallel to the evolution of India’s military culture.
- This was used as command tools during the British era, and as the armed forces evolved, the bugle retained its position of honour, becoming the lead instrument in most regimental bands.
Geographical Indication Tag
- A Geographical Indication tag certifies that the product comes from a specific region and carries unique characteristics, craftsmanship, or reputation.
- The GI tag was associated with sustained government support—marketing assistance, online marketplace access, training for younger craftsmen, and easier credit facilities.
Source: IE
G-Secs
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- Recently, G-Sec yields have inched upward even though the RBI has cut the repo rate.
About G-Secs
- Overview: Government Securities, commonly known as G-Secs, are tradable debt instruments issued by the Central Government or State Governments of India to borrow funds from the public to finance fiscal deficits and public spending.
- Types: G-Secs are broadly classified into Treasury Bills (T-Bills), which are short-term securities with maturities less than one year, and Dated Securities or Government Bonds with maturities of one year or more. State Governments issue bonds called State Development Loans (SDLs).
- Issuance: These securities are issued primarily through auctions conducted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on its electronic platform E-Kuber.
Source: BL
Central Industrial Security Force (CISF)
Syllabus: GS3/Internal Security
In News
- Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) has been designated as a Recognised Security Organisation (RSO) for seaports under the International Ship and Port Facility Security (ISPS) code.
- India has about 250 seaports, of which 65–68 handle active cargo operations.
About Central Industrial Security Force (CISF)
- It was formed in 1968, has grown from 3,129 personnel to 2.2 lakh, making it a multi-faceted Central Armed Police Force deployed nationwide.
- It secures 361 critical installations, including 70 airports, nuclear and space facilities, seaports, power plants, Delhi Metro, Parliament House, government buildings, monuments, and VIPs.
- It is the only CAPF with a dedicated Fire Wing, equipped for advanced firefighting and rescue, and also provides consultancy services to institutions like SBI Data Centres, AIIMS, IIM Indore, and Kashi Vishwanath Temple.
- It is Known as the “Shield of Security” and has the largest number of women personnel among CAPFs, reflecting inclusivity.
Source: TH
Next article
IBSA Dialogue Forum and Equitable Global Governance