
New Monoclonal Antibody Shows Early Promise Against Malaria
Syllabus: GS2/ Health, GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- A novel monoclonal antibody (mAb) named MAM01, has demonstrated strong, dose-dependent protection against malaria in an early clinical trial.
What are Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)?
- Monoclonal antibodies are lab-engineered proteins designed to target specific antigens (foreign substances like viruses, bacteria, or cancer cells).
- They are derived from a single clone of a B-cell and hence are identical in structure and specificity.
- mAbs mimic the natural immune response but are highly specific, making them powerful tools in treating diseases.
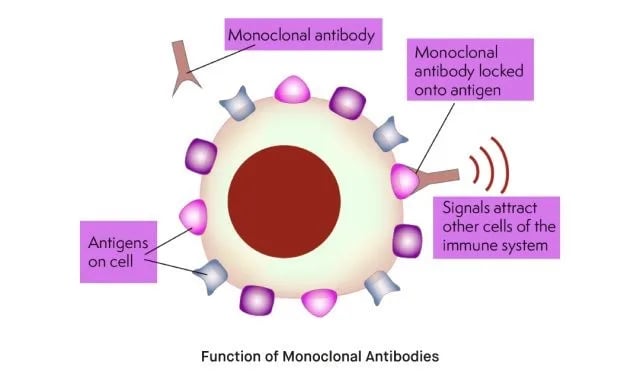
- MAM01 targets a highly conserved region of the Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein (CSP), which enables it to block infection before the malaria parasite reaches the bloodstream.
| What is Malaria? – Malaria is a life-threatening disease spread to humans by some types of mosquitoes. It is mostly found in tropical countries. – Transmission: It is caused by plasmodium protozoa. The plasmodium parasites spread through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. Blood transfusion and contaminated needles may also transmit malaria. – Types of parasites: There are 5 Plasmodium parasite species that cause malaria in humans and 2 of these species – P. falciparum and P. vivax – pose the greatest threat. The other malaria species which can infect humans are P. malariae, P. ovale and P. knowlesi. 1. P. falciparum is the deadliest malaria parasite and the most prevalent on the African continent. P. vivax is the dominant malaria parasite in most countries outside of sub-Saharan Africa. – Symptoms: Fever and flu-like illness, including chills, headache, muscle ache and fatigue. |
Source: DD News
India’s Kabul Mission is Upgraded to Embassy
Syllabus: GS/IR
In News
- India has upgraded its Technical Mission in Kabul to a full-fledged Embassy with immediate effect, following the recent visit of the Taliban administration’s acting Foreign Minister Amir Khan Muttaqi to India.
Background
- India had shut its embassy in Kabul and withdrew the existing staff in August 2021 when law and order had broken down as the Taliban overthrew the government of President Ashraf Ghani.
- The Indian consulates in Mazaar-i-Sharif, Jalalabad, Kandahar and Herat had also been closed as the conflict intensified in early 2021.
- India had sent a technical team to Kabul to run the mission on June 23, 2022 which was meant to facilitate humanitarian assistance and provide consular assistance.
- Multiple major powers such as Iran, China, Russia, Gulf countries and Central Asian republics have engaged the Taliban but Russia alone has granted recognition to the Taliban as the de jure ruler of Afghanistan.
Importance of latest Developments
- The upgraded Embassy will enhance India’s support for Afghanistan’s development, humanitarian aid, and capacity-building efforts in line with the Afghan people’s priorities.
- A chargé d’affaires will be appointed to head the embassy until a formal ambassador is named.
Source:TH
Net FDI inflow fell by 159%
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
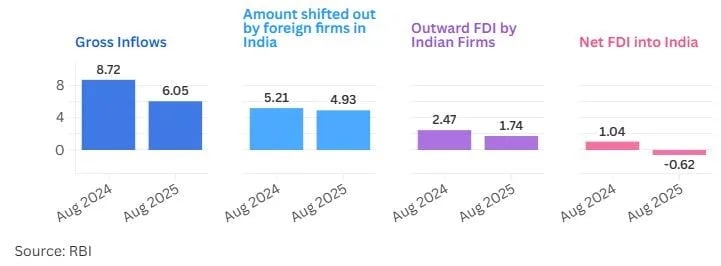
- Net Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into India fell 159% in August 2025, this is the second time this financial year that outflows have exceeded inflows.
About
- Gross investments into India stood at $6,049 million in August 2025, 30.6% lower than their level in August last year.
- Net FDI in the April-August 2025 period was $10,128 million, more than 121% higher than in the same period of last year.
Net Foreign Direct Investment
- Net FDI is gross FDI, which is the total money coming in, minus the money being repatriated out by foreign companies doing business in India and the outward FDI by Indian companies.
- Net FDI = Gross FDI Inflows − (Repatriation by foreign firms + Outward FDI by Indian firms).
- Key Components:
- Gross FDI Inflows: Total new investments made by foreign entities into the country. It includes setting up factories, acquiring local companies, or expanding operations.
- Repatriation & Disinvestment: Profits or capital that foreign companies send back to their home countries. Includes sale of assets or shares in domestic firms.
- Outward FDI: Investments made by domestic companies in foreign countries (e.g., acquisitions, setting up subsidiaries).
- Positive Net FDI: Indicates more foreign investment is coming in than going out, often seen as a sign of economic attractiveness.
- Low or Negative Net FDI: May suggest capital is being withdrawn or domestic firms are investing more abroad than foreigners are investing locally.
Why Net FDI Matters?
- Indicator of Investor Confidence: Positive net FDI shows foreign investors trust the country’s economic and policy environment.
- Source of Stable Capital: FDI is long-term and less volatile than portfolio flows, helping maintain economic stability and balance of payments.
- Boosts Production and Employment: Brings capital, technology, and management expertise, enhancing manufacturing, productivity, and job creation.
- Supports External Sector and Currency: Improves foreign exchange reserves, strengthens the rupee, and helps finance the current account deficit.
Source: TH
UDAN Scheme
Syllabus: GS3/Infrastructure
Context
- Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik (UDAN) scheme has completed 9 Years.
About
- It is a regional connectivity scheme launched in 2016.
- The first UDAN flight operated between Shimla and Delhi in 2017.
- Ministry: Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Aim: To make air travel affordable and accessible to the common citizen by connecting unserved and underserved Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities to major hubs.
- Implementation:
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF): Financial support to airlines to ensure affordable fares.
- Airfare Cap to ensure affordability.
- Collaborative Governance between Centre, States, Airport Authority of India (AAI), and private airport operators.
Achievements
- It has facilitated over 1.56 crore passengers through 3.23 lakh flights in nine years.
- 649 routes have been operationalised connecting 93 unserved and underserved airports, including 15 heliports and 2 water aerodromes.
- The government has also introduced Comprehensive Guidelines for Seaplane Operations last year and launched UDAN 5.5, a special bidding round for seaplanes and helicopters.
Source: AIR
Gallantry Awards
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- President Droupadi Murmu approved 127 Gallantry awards and 40 Distinguished Service awards to the Armed Forces.
About Gallantry Awards
- Gallantry Awards are given by the Government of India to honour acts of bravery, sacrifice, and exceptional courage by members of the armed forces, paramilitary forces, and civilians.
- They are classified as wartime (gallantry in the face of enemy) and peacetime awards.
- Administered by: Ministry of Defence (for armed forces) and Ministry of Home Affairs (for police and civilians).
- Awarded by: President of India.
- These gallantry awards are announced twice in a year – first on the occasion of the Republic Day and then on the occasion of the Independence Day.
- Wartime Gallantry Awards: Param Vir Chakra (PVC), Mahavir Chakra (MVC) and Vir Chakra.
- These were instituted on 26 January 1950, and were deemed to have effect from 15 August 1947, the date of India’s independence.
- Peacetime Gallantry Awards: Ashok Chakra, Kirti Chakra, Shaurya Chakra.
- The Government instituted three more gallantry awards on 4 January 1952, also with retrospective effect from 15 August 1947.
- Originally, they were named as: Ashoka Chakra Class-I, Ashoka Chakra Class-II and Ashoka Chakra Class-III.

- Order of Precedence: Param Vir Chakra (PVC), Ashoka Chakra (AC), Maha Vir Chakra (MVC), Kirti Chakra (KC), Vir Chakra (VrC), Shaurya Chakra (SC).
- All six awards can be conferred posthumously.
Source: AIR
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
Syllabus: GS3/Security Forces
In News
- The Supreme Court transferred the investigation into the Karur stampede from the Tamil Nadu Police Special Investigation Team (SIT) and the Justice Aruna Jagadeesan Commission to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- It is a central agency governed by the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946 which traces its origins to the Special Police Establishment (SPE) formed in 1941 to weed out corruption in war-time procurements.
- It is functioning under Dept. of Personnel, Ministry of Personnel, Pension & Public Grievances, Government of India.
- It is the premier investigating police agency in India.
- It is an elite force playing a major role in preservation of values in public life and in ensuring the health of the national economy.
- It is also the nodal police agency in India, which coordinates investigations on behalf of Interpol Member countries.
Jurisdiction
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) derives its authority from the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946.
- Initially created to investigate corruption in war-time procurement, the DSPE had jurisdiction limited to Union Territories, but under Section 5(1), its jurisdiction can be extended to States and Railway areas with the consent of the State Government as per Section 6.
- The CBI can only investigate cases notified by the Central Government under Section 3, and its officers (Sub-Inspector and above) have the same powers as a station house officer for investigation purposes.
Source: TH
Police Commemoration Day
Syllabus: GS3/Internal Security
Context
- Police Commemoration Day was observed on 21st October at the National Police Memorial to honour the valour and sacrifice of police personnel.
About
- On October 21, 1959, Indian policemen were martyred in an ambush by Chinese troops at Hot Springs, Ladakh.
- The day commemorates their supreme sacrifice and all police personnel who have laid down their lives in the line of duty.
- A memorial was erected at Hot Springs and members of Police Forces from different parts of the country trek to Hot Springs to pay homage to the martyrs.
- Since the year 2012, the Police Commemoration Day Parade has been held at the National level at the Police Memorial.
National Police Memorial (NPM)
- Dedicated by: Prime Minister on Police Commemoration Day, 2018.
- Location: Chanakyapuri, New Delhi.
- The Memorial gives police Forces a sense of national identity, pride, unity of purpose, common history and destiny.
- It comprises a Central Sculpture, a Wall of Valour and a museum.
- The Wall of Valour: 30 feet tall granite sculpture stands at the police memorial with the names of over 35,000 martyrs who sacrificed their lives in the line of duty.
| Do you know? – ‘Police’ and ‘Public Order’ are state subjects under the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India, and various initiatives have been undertaken to modernise police forces. – SMART Policing: The SMART Policing Initiative was introduced by the Prime Minister of India in 2014 to modernize and transform Indian policing in response to emerging security challenges. 1. SMART stands for Strict and Sensitive, Modern and Mobile, Alert and Accountable, Reliable and Responsive, Tech-savvy and Trained. – Assistance to State & UTs for Modernization of Police (ASUMP) Scheme: The erstwhile Scheme of Modernisation of State Police Forces (MPF), ASUMP’s objective is to strengthen police infrastructure at the cutting-edge level by equipping it with the latest technology, weaponry, communication equipment, etc – ‘CyTrain’ portal: It is a Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) platform, developed for capacity building of police officers/judicial officers through online courses on critical aspects of cybercrime investigation, forensics, prosecution, etc. – Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children (CCPWC): Financial assistance under the CCPWC Scheme has been provided to the States/UTs for their capacity building. |
Source: AIR