Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) nuclear fusion reactor has breached a major fusion limit by firing plasma beyond its usual operational range.
About
- They pushed plasma density 65% beyond a special threshold, entering a stable state that overcomes a long-standing barrier to achieving burning plasma, the stage where a fusion reaction becomes self-sustaining.
- This matters for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), the fusion experiment in which India has invested.
Artificial Sun
- It is a nuclear fusion reactor facility, and it is called an “artificial sun” because it mimics the nuclear fusion reaction that powers the real sun – which uses hydrogen and deuterium gases as fuel.
- Scientists generally use a donut-shaped reactor called a tokamak in which hydrogen variants are heated to extraordinarily high temperatures to create a plasma.
- EAST is a testbed reactor for (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) ITER, an international megaproject.
- Members of the Project: The European Union, China, India, Japan, Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- They are working together to build a tokamak that will sustain nuclear fusion that releases more energy than that required to sustain the plasma.
- A tokamak is a machine that uses magnetic fields to confine plasma for nuclear fusion research.
Background
- 1939: Lise Meitner and Otto Frisch explained fission as a process of energy release.
- 1942: The first sustainable nuclear fission reactor was built by Enrico Fermi and team.
- Nuclear fission produces harmful radioactive waste whereas nuclear fusion doesn’t.
- Nuclear fusion reactors have become an important technological goal for a world keenly interested in new sources of clean energy.
- Current Progress: Projects like ITER are working on creating viable fusion reactors, but net-positive energy from fusion is still a work in progress.
What is Nuclear Fusion?
- Nuclear fusion is the process by which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a single heavier one while releasing massive amounts of energy.
- Fusion reactions take place in a state of matter called plasma — a hot, charged gas made of positive ions and free-moving electrons with unique properties distinct from solids, liquids or gases.
- The sun, along with all other stars, is powered by this reaction.
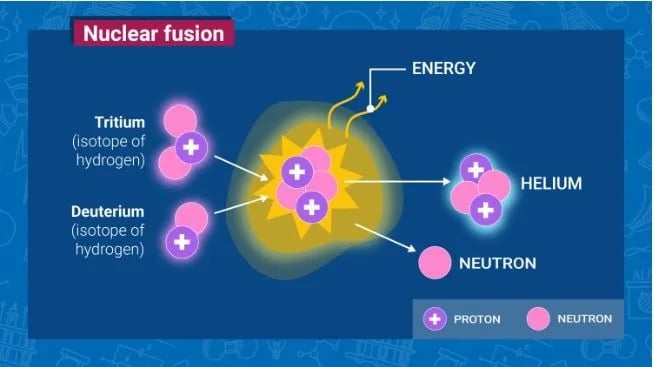
- Process: The Deuterium (H-2) and Tritium (H-3) atoms are combined to form Helium (He-4). A free and fast neutron is also released as a result.
- The neutron is powered by the kinetic energy converted from the ‘extra’ mass left over after the combination of lighter nuclei of deuterium and tritium occurs.
Significance of Fusion Energy
- Clean Energy: Nuclear fusion — just like fission — does not emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, so it could be a long-term source of low-carbon electricity from the second half of this century onwards.
- More Efficient: Fusion could generate four times more energy per kilogram of fuel than fission (used in nuclear power plants) and nearly four million times more energy than burning oil or coal.
- Fusion fuel is plentiful and easily accessible: Deuterium can be extracted inexpensively from seawater, and tritium can potentially be produced from the reaction of fusion-generated neutrons with naturally abundant lithium.
- These fuel supplies would last for millions of years.
- Safer to Use: Future fusion reactors are also intrinsically safe and are not expected to produce high activity or long-lived nuclear waste.
- Furthermore, as the fusion process is difficult to start and maintain, there is no risk of a runaway reaction and meltdown.
Way Ahead
- EAST’s successes are crucial for ITER’s future, which faces criticism for delays and cost overruns.
- High costs have deterred some governments from pursuing such projects.
- The findings suggest a practical and scalable pathway for extending density limits in tokamaks and next-generation burning plasma fusion devices.
Source: TH
Previous article
First Fully Organic Village of Rajasthan