Syllabus: GS3/ Energy
Context
- According to the Department of Atomic Energy, NPCIL has, for the first time, crossed 50 billion units (BUs) of electricity generation in FY 2024–25.
Nuclear Power in India
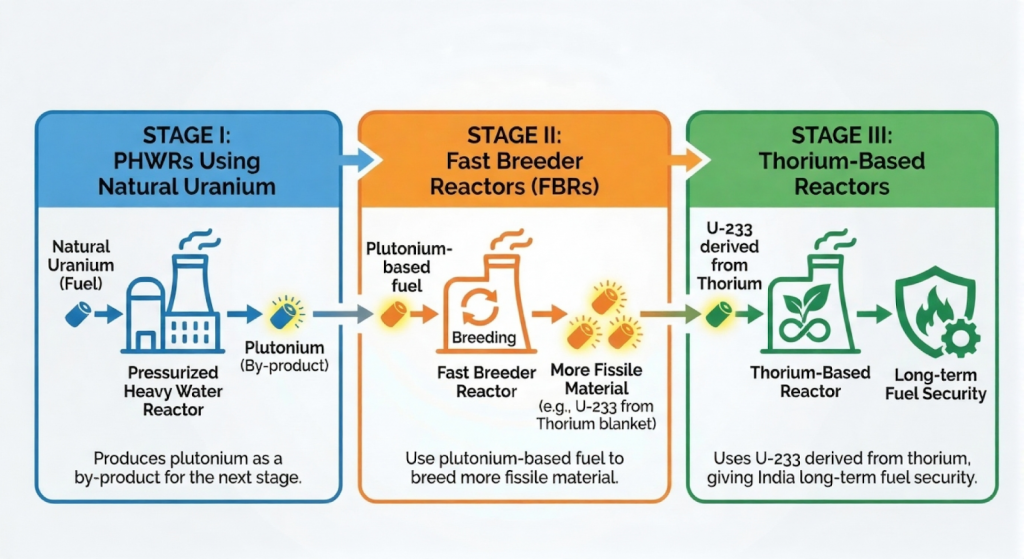
- India operates one of the world’s most unique nuclear programmes based on a three-stage nuclear strategy designed to utilise India’s abundant thorium reserves.
- The current installed nuclear power capacity in the country is around 8.78 GW, spread across 24 nuclear power reactors.
- As of July 2025, nuclear energy contributes around 3.1 % of total electricity generation.
What is Nuclear Energy?
- Nuclear energy is the energy released during nuclear reactions, either through fission (splitting of atomic nuclei) or fusion (merging of atomic nuclei).
- In nuclear fission, heavy atomic nuclei, such as those of uranium or plutonium, are split into lighter nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy.
- This process is utilized in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
Government initiatives for nuclear expansion
- Nuclear Energy Mission: The government has set an ambitious target to increase the country’s nuclear power capacity to 100 GW by 2047
- India had announced a Rs 20,000 crore R&D mission for development of small modular reactors (SMRs). India is also targeting the deployment of at least five of these indigenously developed reactors by 2033.
- NPCIL and National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) have signed a supplementary Joint Venture agreement to develop nuclear power facilities in the country.
- The JV named ASHVINI will build, own, and operate nuclear power plants, including the upcoming 4×700 MWe PHWR Mahi-Banswara Rajasthan Atomic Power Project.
- Unit 7 of the Rawatbhata Atomic Power Project was connected to the Northern Grid and began commercial operations.
- The Atomic Energy Commission approved pre-project activities for ten additional 700 MWe PHWRs, beyond the 22.5 GW nuclear capacity planned by 2032.
Applications of Nuclear Technologies
- Agriculture and Food Processing: DAE developed two new crop varieties: TBM-9, an early-maturing banana, and RTS-43, a high-yield sorghum.
- Advances in Strategic Sectors:
- The Heavy Water Board achieved 99.8% enrichment of Boron-11, suitable for semiconductor applications.
- The first experimental run of India’s dark matter search project, InDEx, began at the Jaduguda Underground Science Laboratory.
Concerns Associated with Nuclear Technology
- High Capital Costs and Long Gestation Period: Nuclear plants require massive upfront investment, making them costlier than solar or wind.
- Radioactive Waste Management: Spent fuel remains hazardous for thousands of years. It requires secure storage, reprocessing, and long-term geological disposal.
- Safety Risks: Catastrophic incidents (Chernobyl, Fukushima) show low-probability but high-impact risks.
- Evacuation, contamination and long-term ecological impacts make public acceptance difficult.
- Water-Intensive Technology: Nuclear reactors require large quantities of water for cooling.
- Not suitable in drought-prone or water-stressed areas.
Way Ahead
- By promoting nuclear energy as a sustainable, scalable, and secure power source, the government aims to bolster energy security and meet the nation’s long-term economic and environmental goals.
- The Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat is poised to accelerate nuclear power development, positioning India as a global leader in advanced nuclear technology by 2047.
Source: DD NEWS