Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) released its first ever ‘Asset Monetization Strategy for the Road Sector’.
About
- NHAI monetizes assets through three modes: Toll-Operate-Transfer (ToT), Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs), and securitisation models.
- These instruments have helped NHAI raise over ₹1.4 lakh crore across more than 6,100 km of National Highways under National Monetisation Pipeline.
What is Asset Monetization?
- Asset monetization, also commonly referred to as asset or capital recycling, is a widely used business practice globally.
- It entails a limited period license / lease of a public sector asset to a private sector entity for an upfront or periodic consideration through a well-defined concession/ contractual framework.
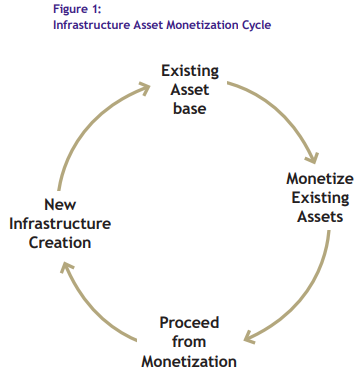
- Hence, it is a virtuous cycle where existing assets are converted into sources of funds, which are then invested in creating new assets.
Pillars of Asset Monetization Strategy
- Value Maximation: The objective of this pillar is to codify and structure processes to systematically identify and offer attractive assets for monetization, so as to increase acceptance of bids that maximize value for the government.
- Transparency: The objective of this pillar is to codify processes that aid transparency both within the organization and in communications with investors.
- Market Development: The objective of this pillar is two-fold;
- Broaden the investor base to attract more private participation.
- Enhance stakeholder engagement to increase traction of NHAI’s asset monetization program.
| Key Monetisation Models Used by NHAI Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) – It is a pooled investment mechanism introduced in 2014 and regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). – How it works: 1. NHAI transfers toll-operating road assets into a trust structure. 2. Investors buy units of the InvIT and earn returns from toll revenues. 3. Includes an Investment Manager (financial returns) and Project Manager (Operations and Management oversight). Toll-Operate-Transfer (ToT) Model – It is a public-private partnership model introduced in 2016. – How it works: 1. Private players pay a lump sum upfront for toll collection rights of completed highways. 2. They also bear the cost of operation and maintenance. Securitization of Toll Revenues – It is project-based financing by using future revenue streams as collateral. – How it works: 1. NHAI creates a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) to raise funds by securitizing future toll receipts. 2. E.g., Delhi-Mumbai Expressway SPV raised ₹40,000 crore using this mechanism. |
Way Ahead
- Scaling Up: More highway projects can be included under the monetisation strategy to unlock additional capital.
- Private Sector Confidence: Ensuring transparent policies and regulatory stability is crucial to boost private participation.
- Capacity Building: Strengthening institutional capacity to structure and manage monetisation deals effectively.
| National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) – The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) is an autonomous agency of the Government of India, set up in 1995, under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH). – NHAI was created through the promulgation of the National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988. – Objective: It is primarily responsible for the development, maintenance, and management of National Highways across the country. – Headquarters: New Delhi |
Source: PIB
Previous article
Bhagwan Birsa Munda