Syllabus: GS3/Environment
In News
- Conservation scientists warn that invasive alien species are destroying local biodiversity and habitats in India.
Invasive alien species
- Definition: They are non-native organisms introduced accidentally or intentionally (e.g., ornamental fish, decorative plants, or for land restoration).
- They often lack natural predators in the new environment, allowing them to multiply unchecked.
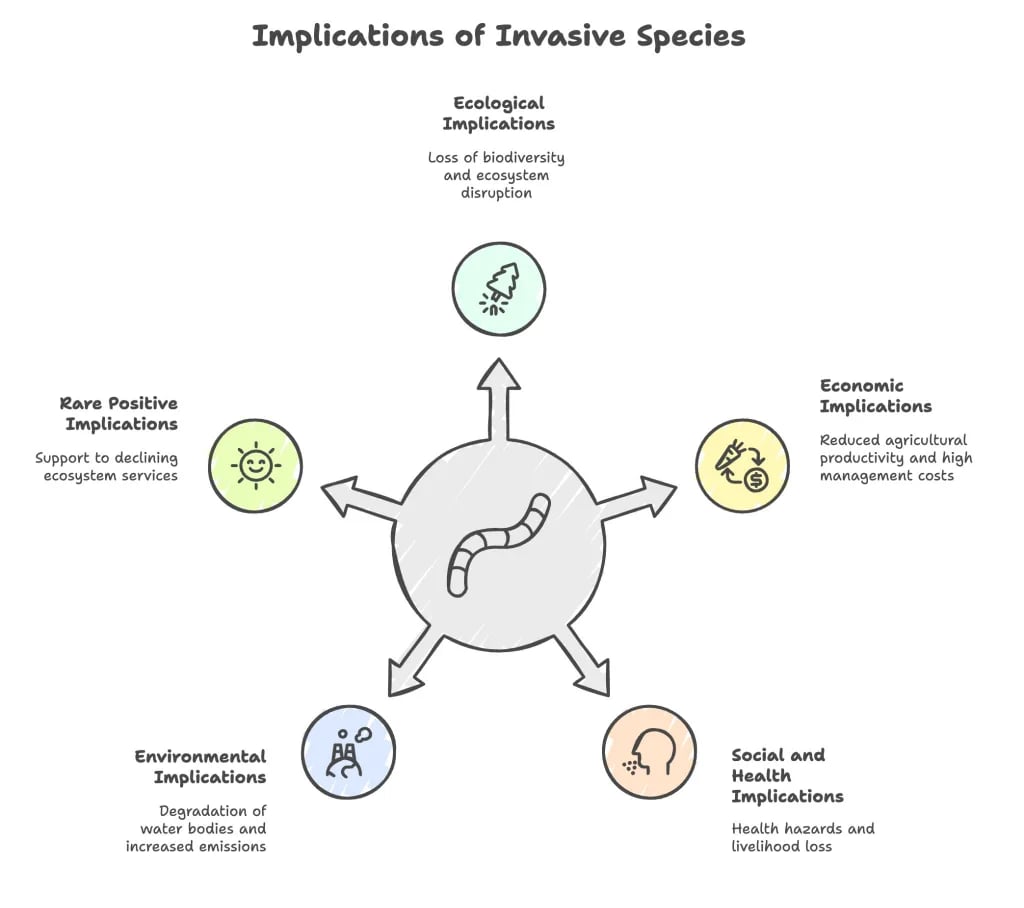
- They often spread rapidly, outcompeting native species, harming biodiversity, causing local or global extinctions, and damaging habitats.
Common Examples in India
- Lantana camara: Invades forests, outcompetes native plants, and hinders regeneration.
- Parthenium hysterophorus (Congress grass): Spreads over farmland and causes allergic reactions.
- Eichhornia crassipes (Water hyacinth): Chokes lakes and rivers, depleting oxygen and affecting fisheries.
- African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus): Outcompetes native fish species, threatening aquatic biodiversity.
Control and Management Measures
- Prevention:
- Stricter quarantine checks on imports, trade, and shipping.
- Ballast water management in ships to prevent marine invasions.
- Control Methods:
- Biological Control: Introducing natural predators, pathogens, or parasites (e.g., insects for Lantana).
- Mechanical Control: Manual removal, cutting, dredging, or uprooting.
- Chemical Control: Use of herbicides or pesticides — applied cautiously to avoid ecological harm.
- Eradication & Restoration:
- Early detection and rapid response for localized infestations.
- Reintroduce native species and restore degraded ecosystems after removal.
Source: TH
Previous article
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2025
Next article
News in Short – 9 October, 2025