
Nauru
Syllabus: GS1/Places in News
Context
- Pacific microstate Nauru, has a novel plan to fund its fight against climate change by selling “golden passports”.
About
- Selling for US$105,000 each, Nauru plans to drum up more than US$5 million in the first year of the “climate resilience citizenship” programme.
- Nauru believes the passport programme could eventually generate $43 million which would account for almost 20% of total government revenue.
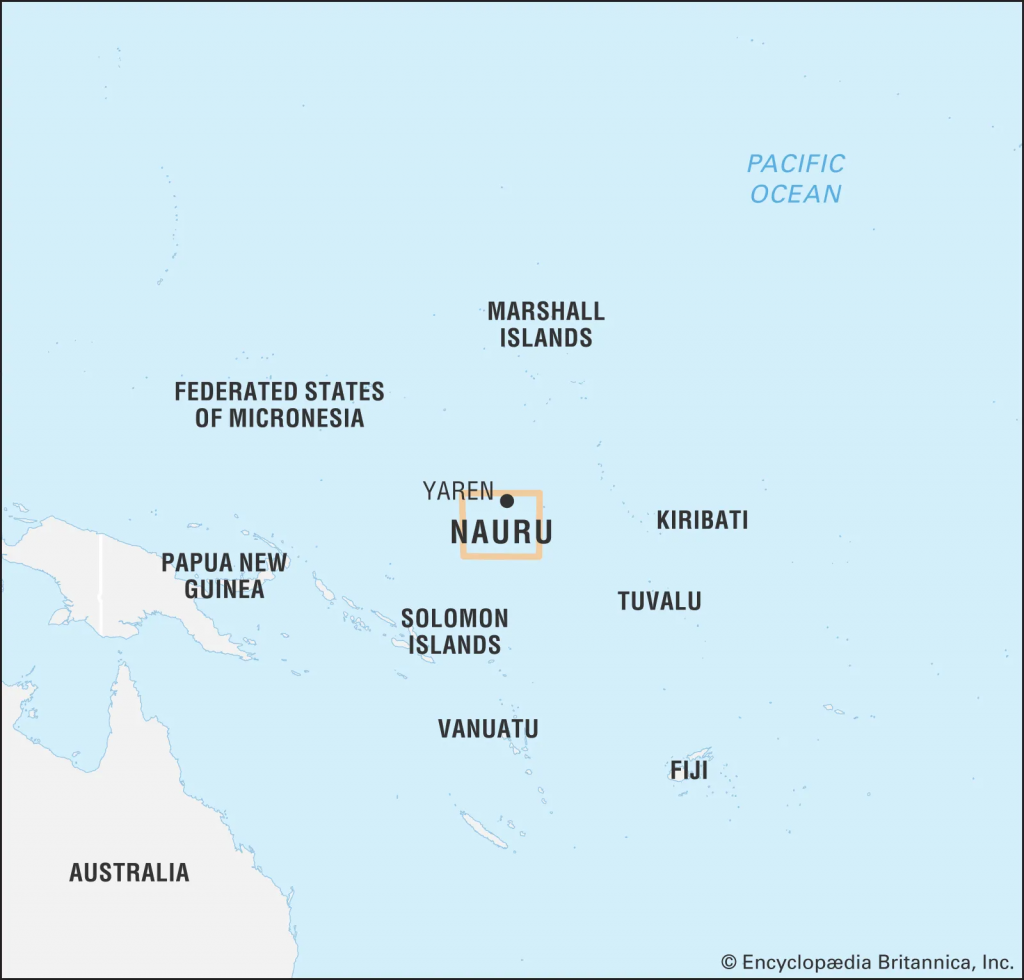
About Nauru
- The island republic of Nauru sits on a small plateau of phosphate rock in the sparsely populated South Pacific.
- It is the world’s third-smallest country by area (21 km²) after Vatican City and Monaco.
- Unusually pure phosphate deposits — a key ingredient in fertiliser — once made Nauru one of the wealthiest places, per capita, on the planet.
- But these supplies have long since dried up, and researchers today estimate 80% of Nauru has been rendered uninhabitable by mining.
- What little land Nauru has left is threatened by encroaching tides as the sea levels are rising 1.5 times faster than global averages.
- Nauru will eventually need to relocate 90% of its population and the first phase of this mass relocation is estimated to cost more than $60 million.
Source: TH
World Trade Organization (WTO)
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
In News
- Brazil has initiated formal consultations at the World Trade Organization (WTO) over US President Donald Trump’s decision to impose 50% tariffs on Brazilian imports, escalating diplomatic tensions between the two nations.
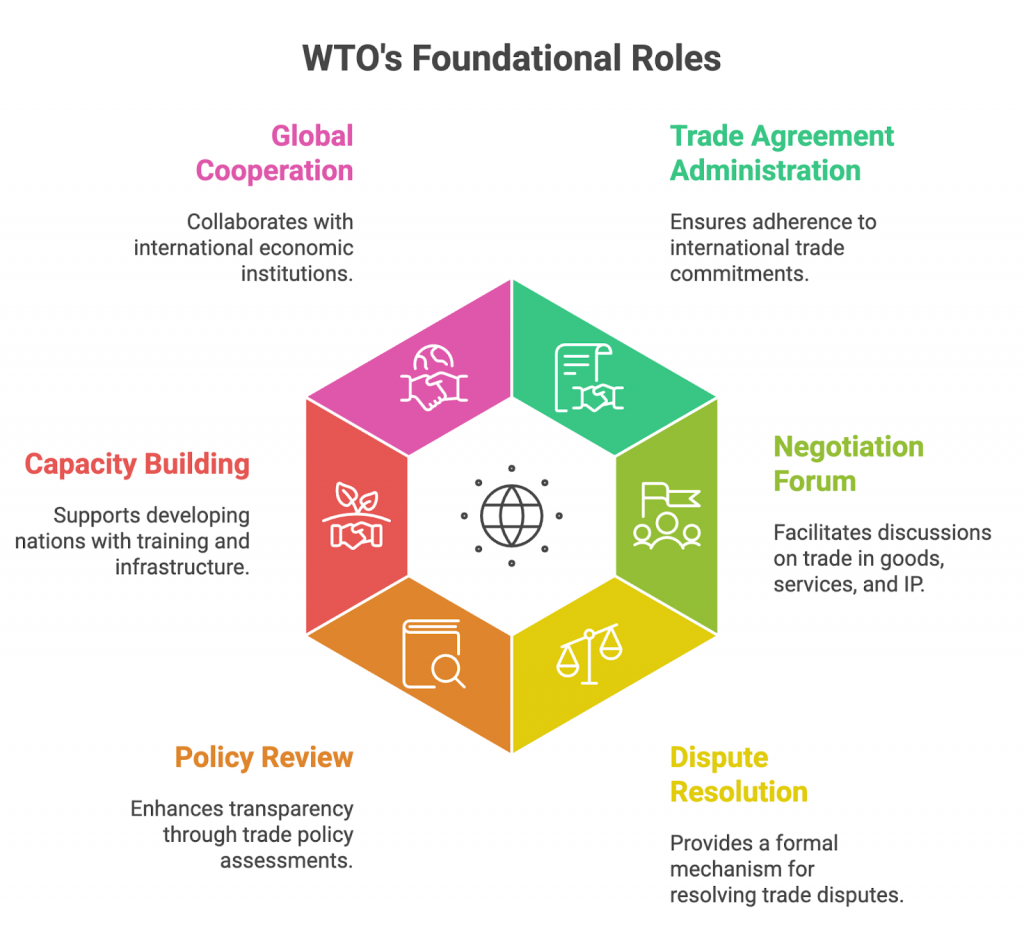
About World Trade Organization (WTO)
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only global international organization responsible for regulating and facilitating trade between nations.
- It was established on January 1, 1995, as the successor to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which had governed global trade since 1948.
- The WTO currently has 166 member countries, representing over 98% of global trade and GDP, and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
Source: TOI
Bharat Forecast System (BharatFS)
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Tech
Context
- India has developed Bharat Forecast System (BharatFS), an advanced weather prediction model that improves extreme rainfall forecasting accuracy by 30% compared to earlier models.
About BharatFS
- BharatFS (Bharat Forecast System) is India’s most advanced real-time global weather prediction model, developed by IITM-Pune in collaboration with NCMRWF-Noida and the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- It is a flagship product of the “Make in India” initiative and supports the Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) vision.
- BharatFS uses the Triangular Cubic Octahedral (TCo) dynamical grid, enabling ultra-high horizontal spatial resolution of 6 km—the highest globally for operational real-time models.
- This is a leap from the previous GFS T1534 model (12 km resolution) and surpasses most leading global models that operate between 9–14 km.
- Its improved resolution allows highly localized forecasts, supporting disaster management and agricultural decision-making down to cluster-of-panchayat/village level.
Significance
- India is currently the only nation running a global, real-time weather prediction system at such high resolution.
- The improved speed and accuracy (with up to a 30% increase in accuracy for extreme rainfall forecasts) make it especially valuable for short- and medium-range weather predictions.
Source: PIB
Understanding Prophylaxis
Syllabus: GS2/Health
In News
- Haemophilia care now focuses on proactive prevention using regular clotting factor replacement or simpler injections, helping maintain joint health, prevent disability, and improve quality of life toward achieving “zero bleeds.”
Hemophilia
- It is a rare bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. This can lead to problems with bleeding too much after an injury or surgery
- There are several different types of hemophilia. The most common are:
- Hemophilia A (classic hemophilia), which is caused by a lack or decrease of clotting factor VIII.
- Hemophilia B (Christmas disease), which is caused by a lack or decrease of clotting factor IX.
Status In India
- In India, only about 20% of the estimated 100,000–150,000 haemophilia cases are diagnosed, due to lack of awareness, limited diagnostics, and socio-economic barriers.
- Untreated bleeds reduce life expectancy and cause significant social and economic challenges such as school absenteeism and unemployment.
Role of Prophylaxis
- It is also known as regular replacement therapy and is the gold standard treatment for haemophilia.
- It aims to prevent bleeding episodes rather than treating them after they occur (as in on-demand therapy).
- It involves frequent clotting factor infusions or newer, easier subcutaneous injections.
Relevence
- Prophylaxis prevents joint damage, enhances quality of life, and reduces healthcare burden by minimizing emergency visits and long-term complications.
- While 90% of patients in developed countries use prophylaxis, most in India still rely on on-demand therapy, though some states have begun implementing regular treatment for children under 10.
- Increasing awareness and access through policy and education is essential to prevent disability and improve lives.
Source :TH
New Lichen Species Discovered in Western Ghats
Syllabus: GS3/Environment and Biodiversity
Context
- A new species of lichen, Allographa effusosoredica, has been discovered in the Western Ghats.
About
- The newly identified species is crustose lichen characterized by effuse soredia and the presence of norstictic acid, a rare chemical trait within the Allographa genus.
- Significance: First Allographa species from India confirmed with molecular data.
- Funded by Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) under project on lichen symbiosis in Western Ghats.
- Taxonomic status in India:
- 53rd Allographa species reported from India.
- 22nd from the Western Ghats.
- The government is actively promoting research and conservation efforts in biodiversity hotspots like the Western Ghats through various policies, initiatives, and funding mechanisms.
Lichens
- Lichens are organisms formed by a partnership between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacterium, where the fungus gives shelter and absorbs water/nutrients, and the alga/cyanobacterium makes food through photosynthesis.
- Types of Lichens (Based on Morphology)
- Crustose: Crust-like, tightly attached to substrate (e.g., Graphis, Allographa).
- Foliose: Leaf-like, loosely attached (e.g., Parmelia).
- Fruticose: Shrub-like, branched (e.g., Cladonia rangiferina).
- Ecological & Economic Importance
- Bioindicators: Very sensitive to air pollution (especially SO₂).
- Soil formation: Break down rocks by secreting acids.
- Food source: For reindeer, insects, snails.
- Medicina/Cosmetic uses: Antibiotics, dyes, perfumes.
- Climate studies: Lichen growth rate used in lichenometry (dating exposed surfaces).
Source: PIB
Karnataka Cabinet Approves Devadasi Rehabilitation Bill
Syllabus:GS2/Governance
In News
- The Karnataka Cabinet has approved the Karnataka Devadasi (Prevention, Prohibition, Relief and Rehabilitation) Bill, 2025, aiming to strengthen efforts against the Devadasi system
Devadasi rehabilitation Bill
- It will replace the 1982 Act and it includes provisions to protect the dignity of Devadasis and their children, such as removing the mandatory declaration of a father’s name on official documents and allowing DNA-based identification.
- It adopts a comprehensive approach by addressing not just prohibition but also offering relief and rehabilitation to Devadasis, responding to long-standing demands for more inclusive legislation.
| Devadasi system – It is an ancient practice dating back to the Chola, Chera, and Pandya dynasties, involving dedicating young lower-caste girls to temple deities. – Though termed “servants of God,” these girls often end up providing sexual services to temple patrons and powerful men. – The system persists under different regional names across India, such as Natis (Assam), Maharis (Kerala), Basavi/Jogati (Karnataka), Jogin (Andhra Pradesh), and Aradhini (Maharashtra). |
Source :TH
Colorado River
Syllabus: GS1/Places in News
Context
- The Colorado River, a vital water source for millions, faces a crisis as its flow diminishes, prompting states to vie for future water rights.
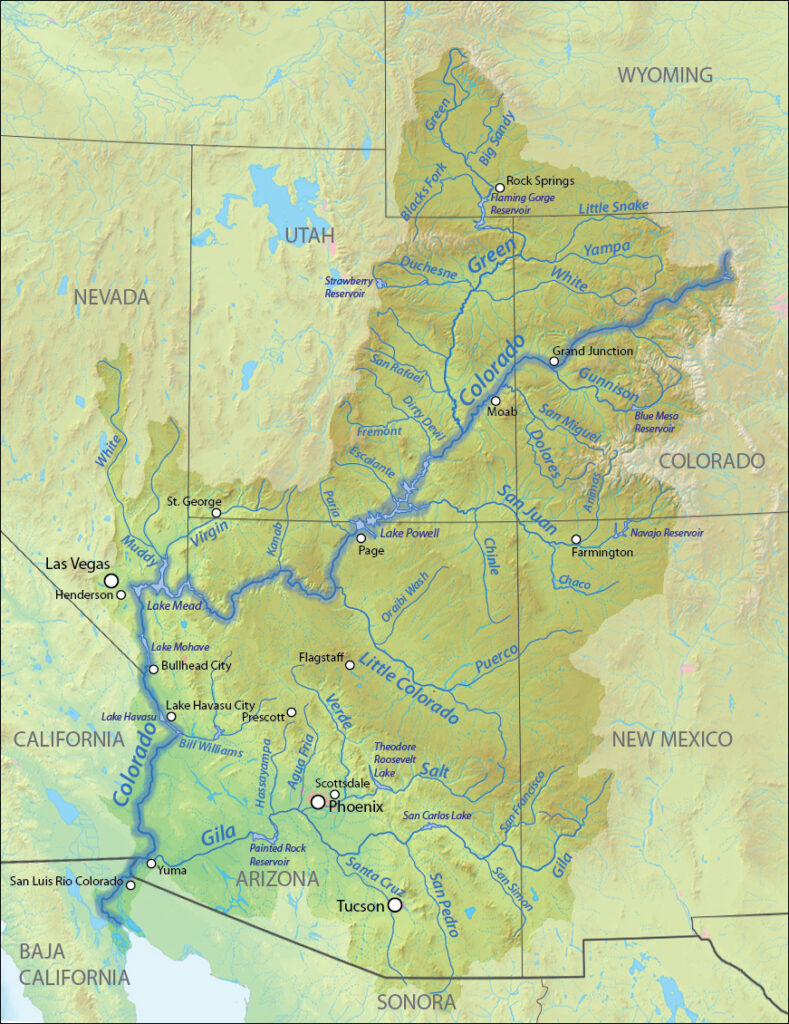
About
- The Colorado River is one of the most important rivers in the western United States and northern Mexico — both ecologically and economically.
- It is also one of the most overused and stressed water systems in the world.
- Source: Rocky Mountains, Colorado (La Poudre Pass).
- Mouth: Gulf of California, Mexico (though it rarely reaches the sea now due to heavy water usage).
- Its drainage basin covers 246,000 square miles (637,000 square kilometres) and includes parts of seven states—Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, Arizona, and California.
Source: DTE
Previous article
Contamination of Ground Water in India
Next article
Quit India Movement