Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- The Nobel Prize in medicine or physiology was announced for three scientists, for their discoveries on peripheral immune tolerance.
- The three scientists Mary Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell and Shimon Sakaguchi shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Human Immune System
- The immune system protects the body from pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- It consists of organs, cells, and molecules that work together to recognize and eliminate harmful substances.
- Major Components of the Immune System:
- Organs: Bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils.
- Cells: White blood cells (leukocytes) — lymphocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, etc.
- Molecules: Antibodies, cytokines, complement proteins.
- These have a role in identifying and eliminating foreign bodies that may bring with it disease.
- However the immune system also identifies cells that have gone rogue – such as in cancerous tumours – or that have mutated in a way that they harm the bodies they constitute.
- Telling apart benign cells from harmful invaders is the key challenge the immune system must negotiate.
What are B and T-Cells?
- B-cells and T-cells are a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes.
- They help the immune system to fight germs and protect from disease.
- Types of T cells:
- Cytotoxic T-cells: They kill cells infected with viruses and bacteria, and they also destroy tumor cells.
- Helper T-cells: They send signals that direct other immune cells to fight infection.
- Regulatory T-cells (Tregs): These cells suppress excessive immune responses to prevent autoimmune reactions and maintain immune tolerance.
- They play a crucial role in preventing the immune system from attacking the body’s own cells and tissues.
- T-cells start in bone marrow, mature in thymus and eventually relocate to lymph tissue or bloodstream.
- B-cells make antibodies in response to antigens (antibody generators).
- There are two main types of B-cells: plasma cells and memory cells. Both types help to protect from infection and disease.
Discovery
- The laureates identified the immune system’s security guards, regulatory T cells, which prevent immune cells from attacking our own body.
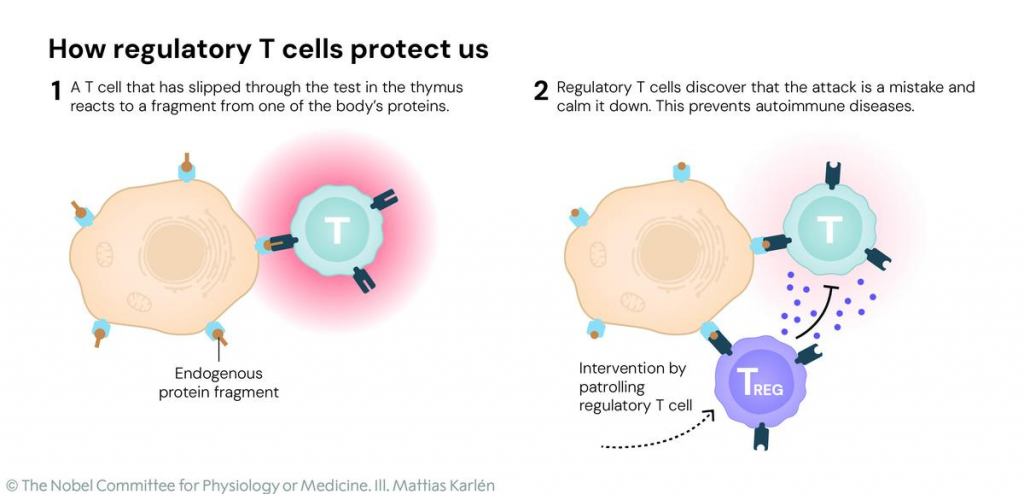
- Their discoveries have been decisive for our understanding of how the immune system functions and why we do not all develop serious autoimmune diseases.
Significance
- The laureates’ discoveries launched the field of peripheral tolerance, spurring the development of medical treatments for cancer and autoimmune diseases.
- Once the function of these new T-cells were known, researchers realised that some tumours can attract a large number of these regulatory T cells, thereby protecting it from the other T cells.
- The discovery of Regulatory T-cells revolutionized immunology by revealing that the immune system is not only attack-oriented but also self-regulating.
- It has major implications for treating autoimmunity, cancer, transplantation, and chronic inflammation.
| About Nobel Prize – Since 1901, the Nobel Prize has been awarded in the fields of physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, literature and peace, while a memorial prize in economic sciences was added in 1968. 1. In 1895 Alfred Nobel gave the largest share of his fortune to a series of the Nobel Prizes. – From Stockholm, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences confers the prizes for physics, chemistry, and economics, the Karolinska Institute confers the prize for physiology or medicine, and the Swedish Academy confers the prize for literature. – The Norwegian Nobel Committee based in Oslo confers the prize for peace. – The Nobel Peace Prize is awarded in Oslo (Norway), while all other prizes are awarded in Stockholm (Sweden). – The Nobel Foundation is the legal owner and functional administrator of the funds and serves as the joint administrative body of the prize-awarding institutions. 1. It is not concerned with the prize deliberations or decisions, which rest exclusively with the four institutions. – Process of Selection: 1. Nominations are invited from qualified individuals (scientists, professors, former laureates, etc.). 2. Selection Committees review and recommend the winners. 3. The final decision is made by the respective Nobel institutions. |
Source: TH
Previous article
Reforming Passive Euthanasia in India
Next article
News in Short – 7 October, 2025