
Amazon’s ‘flying rivers’
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
In News
- The Amazon rainforest plays a critical role in South America’s water cycle through the phenomenon called “flying rivers”.
About Flying Rivers
- “Flying rivers” are massive streams of water vapour carried in the atmosphere, invisible to the eye.
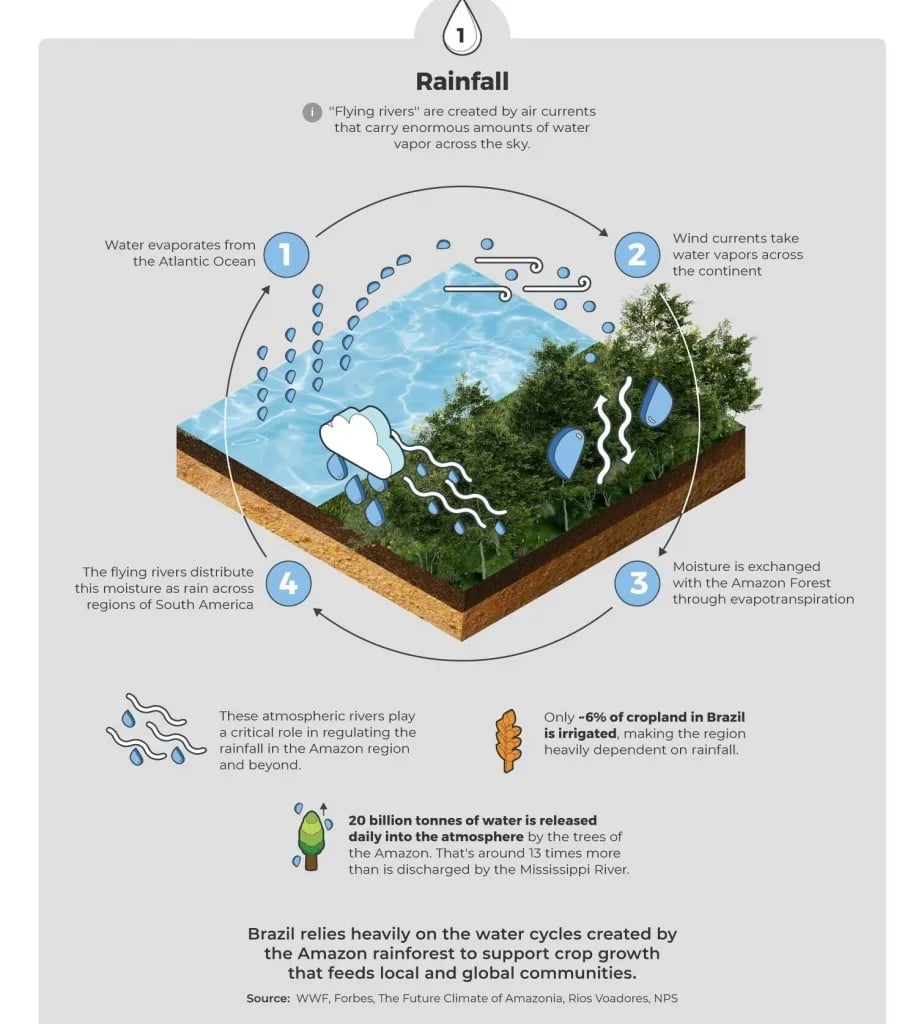
- Process:
- Moisture originates from the Atlantic Ocean.
- Trade winds push moist air westward across the equator.
- Amazon trees act as a “biological pump” – absorb water from soil → transpire it back into the air → release huge amounts of water vapour.
- This recycled water forms clouds and rainfall further inland, supplying regions as far as the Andes and southern South America.
Source: IE
Sir Creek
Syllabus: GS1/Places
In News
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh warned Pakistan that any aggression in the disputed Sir Creek area will be met with a strong response.
What is Sir Creek region?
- Sir Creek is a 96-km-long tidal estuary or a “fluctuating tidal channel” between Gujarat’s Rann of Kutch and Pakistan.
- The Rann lies on the border between Gujarat and the Pakistani province of Sind.
- It is considered a disputed region due to varying interpretations of maritime boundary lines by both sides.
- Sir Creek is a strategic and sensitive zone along the Gujarat coastline
Disputes
- The Sir Creek dispute between India and Pakistan revolves around the interpretation of the maritime boundary in the marshy estuarine region between Gujarat and Sindh.
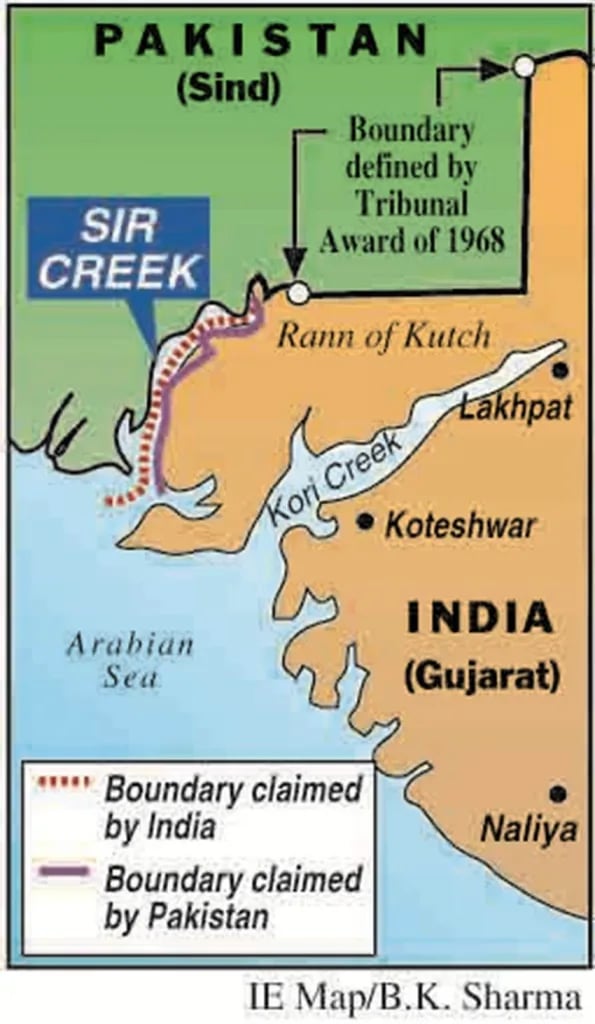
- Originating from a pre-independence disagreement between the princely states of Kutch and Sind over territorial claims, the issue was addressed in a 1914 resolution invoking the thalweg principle—setting boundaries along the mid-channel of navigable waters.
Stand of both countries
- India supports this principle, citing navigability during high tide and historical maps, while Pakistan argues that Sir Creek is a tidal estuary and not navigable, thus rejecting the thalweg’s applicability.
- The dispute gained prominence post-1965 and was partially resolved by the 1968 Indo-Pakistani Western Boundary Case Tribunal, which upheld most of India’s claims over the Rann of Kutch.
- However, the boundary from the mouth to the top of Sir Creek and eastward to the Western Terminus remains contested.
Source :TH
DigiLocker
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) has announced that candidates’ documents, including caste, income, and disability certificates, will now be verified through DigiLocker.
About DigiLocker
- DigiLocker is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY) under Digital India programme.
- DigiLocker aims at ‘Digital Empowerment’ of citizens by providing access to authentic digital documents to citizen’s digital document wallet.
- The issued documents in DigiLocker system are deemed to be at par with original physical documents as per Rule 9A of the Information Technology (Preservation and Retention of Information by Intermediaries providing Digital Locker facilities) Rules, 2016.
Benefits to Agencies
- It reduces the administrative overhead by minimizing the use of paper and curtailing the verification process.
- Digital Transformation: Issued Documents available via DigiLocker are fetched in real-time directly from the issuing agency.
- Secure Document Gateway: Acts as a secure document exchange platform like payment gateway between trusted issuer and trusted Requester/Verifier with the consent of the citizen.
Source: IE
Hike in Wheat MSP
Syllabus: GS3/ Agriculture
Context
- The Union Cabinet, approved a 6.59% increase in the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for wheat to Rs 2,585 per quintal for 2026-27 marketing year.
What is MSP?
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) is a form of market intervention by the Government of India to insure agricultural producers against any sharp fall in farm prices.MSP protects the producer- farmers against distress sale during bumper production years.
- MSPs have no statutory backing — a farmer cannot demand MSP as a matter of right.
Crops Covered
- The Centre announces the MSP for 22 mandated crops.These include:
- 14 kharif crops (paddy, jowar, bajra, maize, ragi, tur/arhar, moong, urad, groundnut, soyabean, sunflower, sesamum, niger seed, cotton),
- 6 rabi crops (wheat, barley, gram, masur/lentil, rapeseed and mustard,and safflower) and
- 2 commercial crops (jute and copra).
- In addition, MSP for Toria and de-husked coconut is also fixed on the basis of MSPs of rapeseed & mustard and copra respectively.
| Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) – FRP is the minimum price at which the sugar mills purchase sugarcane from farmers. – The Cabinet Committee of Economic Affairs announces the FRP on the recommendations of CACP. |
Who decides what the MSP would be and how?
- The Cabinet Committee of Economic Affairs announces the MSP at the start of each sowing season, taking into account the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- While recommending MSPs, the CACP looks at following factors:
- the demand and supply of a commodity;
- its cost of production;
- the market price trends (both domestic and international);
- inter-crop price parity;
- the terms of trade between agriculture and non-agriculture (that is, the ratio of prices of farm inputs and farm outputs);
- a minimum of 50 per cent as the margin over the cost of production; and
- the likely implications of an MSP on consumers of that product.
| Condition for Wheat Cultivation – Climate: Temperature: Requires 10-15°C during sowing (germination) and 21-26°C during ripening and harvesting. 1. Rainfall: Optimal rainfall is 50-100 cm. Excess rainfall can damage the crop. 2. Sunlight: Requires bright sunshine during the ripening period. 3. Frost & Hailstorm: Sensitive to frost at the flowering stage and susceptible to damage from hailstorms. – Soil: Type: Grows best in well-drained loamy and clayey soil. 1. pH Level: Prefers slightly alkaline to neutral soil (6-8 pH). |
Source: TH
Biomedical Research Career Programme
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- The Union Cabinet has approved Phase-III (2025-26 to 2030-31) of the Biomedical Research Career Programme (BRCP) to significantly boost India’s biomedical research ecosystem and global impact.
About
- The programme aims to strengthen research systems, reduce regional disparities in scientific capabilities, and establish world-class biomedical research capacity with a strong global presence and impact.
- BRCP is implemented through a partnership between the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India; the Wellcome Trust (WT), United Kingdom; and the India Alliance—a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) created for this initiative.
Source: PIB
Centre Withdraws Approval for Animal Protein-based Biostimulants
Syllabus: GS3/ Science & Technology
In News
- The Centre has withdrawn approval for 11 animal protein-based biostimulants in India due to religious and dietary concerns.
About Biostimulants
- A biostimulant is a substance, microorganism, or mixture that promotes plant growth by:
- Stimulating natural physiological processes
- Improving nutrient uptake and efficiency
- Enhancing tolerance to abiotic stresses such as drought or heat
- Common examples include humic acids, seaweed extracts, composted liquid manure, and beneficial bacteria and fungi.
- Biostimulants are officially categorized as distinct from fertilizers and insecticides—they neither supply nutrients directly like fertilizers nor control pests like pesticides.
- The Fertilizer (Inorganic, Organic or Mixed) (Control) Order, 1985 regulates biostimulants separately from fertilizers and pesticides, with stricter norms introduced post-2021.
Source: TH
US Tomahawk Missiles
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
Context
- Ukraine has requested long-range Tomahawk cruise missiles from the United States.
What are Tomahawk missiles?
- Tomahawks are long-range subsonic cruise missiles that can be launched from ships, submarines or ground launchers.
- They have long-range, deep-strike capabilities, and can hit targets 1,250km-2,500km away.
- They carry high-explosive warheads designed to penetrate hardened targets like military bunkers.
- They avoid radar detection by flying at high subsonic speeds while maintaining low altitudes.

Source: ET
Previous article
Polar Geoengineering