Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- The Economic Survey 2024-25 highlights the connection between mental health and the country’s economic future, emphasizing its impact on productivity, economic growth, and overall well-being.
- The survey highlights how mental well-being influences workplace efficiency, lifestyle choices, and national economic progress.
Understanding Mental Wellbeing
- The survey defines mental well-being as a multidimensional concept that includes:
- Emotional health: Managing stress and emotions effectively.
- Social health: Building healthy relationships and a supportive community.
- Cognitive health: Enhancing focus, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities.
- Physical health: Maintaining overall fitness through a healthy lifestyle.
Rise in Mental Health Issues Among Youth
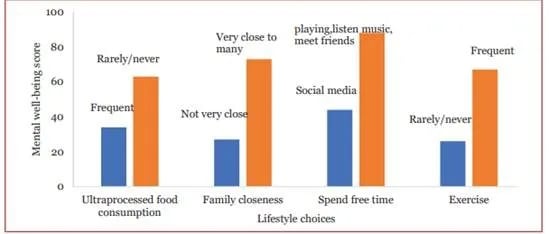
- The survey highlights the rising mental health concerns among India’s youth due to:
- Excessive internet & social media use: Leads to anxiety, sleep disorders, and attention issues.
- Lack of family engagement: Weak social support systems negatively impact emotional well-being.
- Hostile workplaces & long working hours: Cause burnout, stress, and reduced productivity.
- Unhealthy lifestyle choices: Ultra-processed foods and lack of physical activity worsen mental and physical health.
Mental Health and Economic Growth
- Hostile work cultures and excessive hours spent working at the desk can adversely affect mental well-being and ultimately put the brakes on the pace of economic growth.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimated that mental health disorders could lead to an economic loss of $1.03 trillion for India between 2012 and 2030.
- India’s demographic dividend is riding on skills, education, physical health and, above all, mental health of its youth.
Suggestions
- A positive work environment can benefit mental health.
- It calls for interventions at both school and family levels to encourage healthier lifestyles.
- Promoting outdoor activities, building friendships, and strengthening family relationships can help reduce internet overuse and improve mental well-being.
| India’s Mental Health Landscape – For the first time ever, the Economic Survey 2023-24 talked about mental health, its significance and implications on policy recommendations. – As per the National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) 2015-16, 10.6% adults in India suffered from mental disorders while treatment gap for mental disorders ranged between 70% and 92%. 1. The prevalence of mental morbidity was higher in urban metro regions (13.5%) as compared to rural areas (6.9%). – Lack of Psychiatrists in India: The World Health Organization’s guidelines state that there should be at least three practising psychiatrists per one lakh population. 1. As per the latest National Mental Health Survey (NMHS) 2015 and 2016, India has only 0.75 psychiatrists per 1 lakh population. Key Initiatives – Mental Healthcare Act, 2017: The act decriminalised suicide attempts in India and also included WHO guidelines in the categorisation of mental illnesses. 1. The most significant provision in the act was “advanced directives”, which allowed individuals with mental illnesses to decide the course of their treatment. 2. It also restricted the use of electro-convulsive therapy (ECT), and banned its use on minors, introducing measures to tackle stigma in Indian society. – Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2017: The Act acknowledges mental illness as a disability and seeks to enhance the Rights and Entitlements of the Disabled. – Kiran Helpline: The helpline is a step towards suicide prevention, and can help with support and crisis management. – District Mental Health Programme (DMHP): Delivered in 767 districts, offering services like suicide prevention, stress management, and counseling. – National Tele Mental Health Programme (NTMHP): Launched in 2022 to provide access to mental health services through 53 Tele MANAS Cells across 36 states/UTs. – Expansion of Mental Health Capacity: Strengthening mental health services and educational resources in medical colleges and hospitals. |
Conclusion
- Mental health is crucial for both personal and societal development.
- Governments, employers, and organizations must continue efforts to improve mental health care access and reduce stigma.
- India is making strides in mental health with policies and programs to address challenges and bridge treatment gaps.
Source: PIB
Previous article
UIDAI Notifies New Rules for Aadhar Authentication