YOJANA December 2023 (Year End Special)
Chapter 1- India’s Growing Stature- A Rising Power
- India has set an example for the rest of the world through its leadership of the G20 through its values-based approach, its emphasis on global cooperation, and a human-centric vision of peace and progress for all.
- It was a big success in building consensus on key issues such as the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), macro-economic stability, digital public infrastructure, climate challenge, a just and equitable green transition, and reforms of multilateral structures.
Indian Leadership
- India is no longer perceived as an observer on the global stage. It is now a key player in shaping outcomes.
- India advocated for ‘One Earth One Family One Future’, ‘leaving none behind’ and the philosophy of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam, by inclusion of the African Union (AU) into the G20 at the New Delhi Summit.
- It helps makes the G20 structure more representative, highlights India’s role as a true friend of the Global South.
- Apart from the vaccine assistance programme during the pandemic, the International Solar Alliance (ISA), the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI), the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), and Infrastructure for Resilient Island States (IRIS) was lead under Indian leadership.
- Green Grids Initiative- One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG), which was proposed by PM Modi at the First Assembly of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) in 2018.
Mission LiFE and Climate Crisis
- Climate change and environmental degradation have emerged as two of the world’s greatest challenges.
- India has pointed to a different path for ameliorating the situation, beyond science, technology, and the exploitative mercantilism.
- India has offered Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), which places individual behaviour at the centre of the global climate action debate.
- Mission intends to propagate a global network of individuals committed to environmentally-friendly lifestyles based on sustainable consumption patterns.
- India is the only G20 country to have achieved its Paris Agreement Goals well before the stipulated target of 2030.
- India has announced ambitious targets for 2030, including installing 500 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity and reducing the emission intensity of its economy by 45 per cent.
Clean Energy
- At the G7 Summit in June 2022, PM Modi highlighted India’s efforts towards clean energy.
- India and the US have together revamped the US-India Strategic Clean Energy Partnership (USISCEP).
- It aims to advance energy security and innovation, scale up emerging clean energy technologies, and deploy technical solutions through five key pillars:
- Responsible Oil and Gas Pillar
- Power and Energy Efficiency Pillar
- Renewable Energy Pillar
- Sustainable Growth Pillar, and
- Emerging Fuels and Technologies.
- India Clean Energy and Climate Partnership (CECP) was established in 2016. This aims to promote clean energy cooperation and the implementation of the Paris Agreement by increasing the deployment of climate-friendly energy sources such as solar and wind energy.
Resilient Supply Chains
- In December 2021, the Government announced a nearly $10 billion production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme to encourage chip manufacturing in India.
- The trilateral Supply Chain Resilience Initiative, launched in collaboration with Australia and Japan, is another significant step in addressing the supply chain crisis.
Digital Infrastructure
- On 1 July 2015, the Prime Minister launched Digital India to transform India into an empowered digital economy.
- Digital India aims to increase the affordability and accessibility of the internet to Indian citizens and also to improve the digital infrastructure across the country.
- As a result of this today, almost all government programmes have a digital dashboard that provides all the details of beneficiaries.
- In 2021, India reported 48 billion real-time digital transactions, or 40 per cent of the global total.
- Around the world, countries have evinced interest in the Indian model of the UIDAI, Aadhaar and the unified payment portals that link India’s huge population into a seamless whole.
Yoga and Ayurveda
- India has supported prevention over cure not only by exporting vaccines but also by promoting healthy living habits.
- India believes in food and traditional practices like yoga as part of medicine that can stimulate the holistic development of an individual.
- Government promoted Ayurvedic medicine or simple home remedies to boost natural immunity.
- India exported medicines and other equipment to help various countries and became the first respondent in the Indian Ocean region.
- Vaccine Maitri helped deliver vaccines to 101 countries.
International Year of Millets
- Government of India proposed to the United Nations that 2023 be declared the International Year of Millets (IYoM-2023).
- It got support from 72 countries, and on 5 March 2021, the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) officially declared 2023 as the International Year of Millets.
- This is a primary food crop in semi-arid tropical regions, where conventional food crops struggle to thrive due to limited rainfall and poor soil quality.
- Millets also boast superior nutritional content in comparison to major cereal crops, contributing to food security and dietary health.
Conclusion -
There has been a tremendous change in India’s trajectory over the last nine years. India has now entered the period of Kartavya Kaal, which will provide a golden opportunity for India to achieve unprecedented levels of scientific, technological, economic, and social progress. Today, India has emerged as a Vishwa Mitra (global friend), a Vishwa Guru (global teacher), and a Vishwa Vaid (global physician) in sharp contrast to many others embroiled in trade, military, or ideological confrontation.Chapter 2- Redefining Mobility-Transforming Landscape of Transport Sector
- The present transport system of the country comprises several modes of transport including rail, road, coastal shipping, air transport etc.
- Transport has recorded substantial growth over the years both in the spread of the network and in output of the system.
Roads
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways was formed in 2009 by bifurcating the erstwhile Ministry of Shipping, Road Transport and Highways into two independent ministries.
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways is the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules, regulations and laws relating to road transport and transport research.
- It encompasses construction and maintenance of national highways (NHs); administration of Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 and Central Motor Vehicles Rules 1989; National Highways Act, 1956 and National Highways Fee (Determination of Rates and Collection) Rules, 2008; formulation of broad policies relating to road transport, environmental issues, automotive norms, etc.
- India has about 62.16 lakh km of road network, which is the second largest in the world.
Bharatmala Pariyojana
- The Pariyojana envisages the development of about 26,000 km length of economic corridors, which, along with the Golden Quadrilateral (GQ) and North-South and East-West (NS-EW) Corridors.
- It is expected to carry majority of the freight traffic on roads.
- It also envisages development of Ring Roads/bypasses and elevated corridors to de-congest the traffic passing through cities and enhance logistic efficiency, etc.
Green National Highways Corridor Project
- It was launched in 2016.
- The project includes upgradation of about 781 km of various national highways passing through Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh.
- The objectives of the project include: to evolve a policy framework for plantation along national highways; to reduce the impact of air pollution and dust as trees and shrubs are known to be natural sinks for air pollutants; to reduce the impact of ever-increasing noise pollution caused due to increase in the number of vehicles; to arrest soil erosion at the embankment slopes.
- The project is being run with World Bank aid.
National Highways Authority of India
- It was set up under the NHAI Act, 1988.
- It has been entrusted with National Highways Development Project (NHDP), which along with other minor projects, has vested in it 50,329 km of national highways for development, maintenance and management.
- It ensures that all contract awards and procurements conform to the best industry practices with regard to transparency of process, adoption of bid criteria to ensure healthy competition in the award of contracts, implementation of projects conform to the best quality requirements, and the highway system being maintained to ensure best user comfort and convenience.
- The total length of NH (including expressways) in the country is 1,32,499 km while highways/expressways constitute only about 1.7 per cent of the length of all roads. They carry about 40 per cent of the road traffic.
National Highways Development Project
- It is a project to upgrade, rehabilitate and widen major highways in the country to a higher standard.
- It was started in 1998.
- It is managed by NHAI under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- It represents 49,260 km of roads and highways work and construction in order to boost economic development of the country.
- The NHDP has been subsumed in the ongoing Bharatmala project.
PM GatiShakti Plan
- It is essentially a digital platform to bring 16 ministries, including Railways and Roadways together, for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity projects.
- It will facilitate the last-mile connectivity of infrastructure and also reduce travel time for people.
- Its important features include: -
- Comprehensiveness: all the existing and planned initiatives of various ministries and departments with one centralised portal.
- Optimisation: It will assist different ministries in planning for projects after identification of critical gaps.
- Analytical: It will provide the entire data at one place with GIS based spatial planning and analytical tools.
- Dynamic: All ministries and departments will now be able to visualise, review, and monitor the progress of cross-sectoral projects, through the GIS platform.
Parvatmala Pariyojana
- It is being implemented for development of ropeways to improve accessibility and convenience for passengers and to promote tourism.
- Along with hilly areas, ropeways are being developed as alternative mode of transportation in congested urban areas e.g., those of Varanasi, Ujjain.
National Registry of Vehicle and License Records
- Transport Mission Mode Project has successfully automated RTO operations, set up a consolidated transport database.
- The salient aspects of this Mission Mode Project are two flagship applications—Vahan and Sarathi.
- Vahan consolidates vehicle registration, taxation, permit, fitness and associated services across the country.
- Sarathi looks after the driving license, learner licence, driving schools and related activities.
- The database is integrated with Aadhaar for biometric authentication and eKYC, integration with DigiLocker.
- This allows use of virtual documents like driving license, registration certificates, permits, etc., as authorised soft copies.
e-Tolling
- National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) is flagship initiative of Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- It has been implemented on pan- India basis in order to ensure seamless movement of traffic through fee plazas.
- It will increase transparency in collection of user fee using FASTag.
- The National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) is the Central Clearing House.
Railways
- First train was steamed off from Mumbai to Thane in 1853 with a distance of 34 km.
- Today, Indian Railways have grown into a vast network of 7,308 stations spread over a route length of 68,043 km with a fleet of 13,215 locomotives.
- It has played a vital role in the economic, industrial and social development of the country.
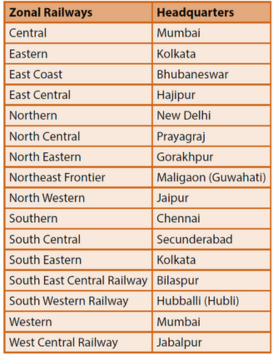
- The network is divided into 17 Zones. Divisions are the basic operating units.
Research and Development
- The Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) at Lucknow is the R&D wing of Indian Railways.
- It functions as a consultant in technical matters.
- It also provides consultancy to other organisations connected with railway manufacture and design.
- It has also developed and designed high speed automobile carrier coaches which has up graded features of loading/unloading of two wheelers, four wheelers, MUVs, SUVs, tractors, etc., with a capability to cater higher payload of 18 tonnes and speed potential of 110 kmph.
Shipping
- Maritime Transport is a critical infrastructure for the economic development of a country.
- The Ministry was renamed as Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Watersays (MoPSW) in 2020.
- The Ministry is also responsible for shipbuilding and ship repair, major ports and inland water transport.
- It is the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws related to shipping.
Maritime Development
- India has a long coastline of about 7,517 km, spread on the western and eastern shelves of the mainland and also along the Islands.
- There are 12 major ports and about 200 non-major ports.
- Approximately 95 per cent of the country’s trade by volume and 68 per cent by value is moved through maritime transport.
Sagarmala Programme
- It aims to promote portled development in the country.
- The vision is to reduce logistics cost of EXIM and domestic trade with minimal infrastructure investment.
- This includes reducing the cost of transporting domestic cargo; lowering logistical cost of bulk commodities by locating future industrial capacities near the coast; improving export competitiveness by developing port proximate discrete manufacturing clusters, etc.

Major Ports
- Ports provide an interface between ocean transport and land-based transport and play a vital role in the overall economic development.
- There are 12 major ports and about 205 non-major ports along India’s coastline which is about 7,517 km.
- The 6 major ports–Kolkata, Paradip, Visakhapatnam, Kamarajar (Ennore), Chennai and VC Chidambaranar, are on the east coast and the other major ports, viz., Cochin, New Mangalore, Mormugao, Mumbai, Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Sheva, Navi Mumbai) and Deendayal (erstwhile Kandla) are on the west coast.
- The major ports are under the direct administrative control of the central government and fall in Union List (7th Schedule of the Constitution).
- Ports other than the major ones are under the jurisdiction of the respective maritime state government and fall in the Concurrent List.
- Of the total traffic handled by all Indian ports, 55 per cent is handled by major ports and 45 by others.
Inland Water Transport
- India has about 14,500 km long navigable inland waterway network.
- Inland Water Transport (IWT) is a fuel-efficient, environment-friendly and cost-effective and lower carbon footprint mode of transport.
- Presently less than 2 per cent of the total cargo movement in the country.
- To promote IWT, Government declared 111 (including 5 existing and 106 new) National Waterways (NWs) spread over 24 states under the National Waterways Act, 2016, to promote inland water transport in the country.
Civil Aviation
- Air transport is one of those sectors which prominently influence economy and employment generation through its direct and catalytic multiplier effects.
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation monitors and control civil aviation sector in the country which includes air transport, air space management, noncommercial flying and civil aviation infrastructure.
- It administers the Aircraft Act, 1934, Aircraft Rules, 1937, Airports Authority of India Act, 1994, Carriage by Air Act, 1972 and other legislations pertaining to the civil aviation sector.
- Ministry is also responsible for implementation of treaties, conventions and agreements relating to the civil aviation sector.
- It enters into Air Services Agreement with other countries for the operation of international scheduled air services.
- The Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS)- Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik (UDAN) was envisaged in National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP) 2016. It aims to facilitate/stimulate regional air connectivity by making it affordable to masses.
- Through measures such as concessions by the central government, state governments/UT administrations and airport operators to reduce the cost of airline operations on regional routes; and Viability Gap Funding (VGF) to meet the gap, if any, between the cost of airline operations and expected revenues on such routes.
Airports Authority of India
- It was constituted under the Airports Authority of India Act, 1994, by merger of erstwhile International Airports Authority and National Airports Authority.
- AAI is responsible for administration and cohesive management of airports and civil enclaves where air transport services are operated/intended to be operated and of all aeronautical communication stations.
- It is also entrusted for the control and management of Indian airspace including provision for air navigation services.
GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN)
- It is a collaborative system developed jointly by Airports Authority of India and Indian Space Research Organization.
- It aims to improve the accuracy and reliability of GPS signals, specifically for precision approaches in civil aviation.
- It has been in full operation since 2015 and is available around the clock.
Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan
- Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan (Accessible India Campaign), is in line with the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
- Ministry of Civil Aviation has published the ‘Accessibility Standards and Guidelines for Civil Aviation Sector’ to assist people comprehend and understand the Universal Accessibility Standards.
- It aims to providing the services at airports by understanding the needs of persons with reduced mobility, old people, children etc. and making air travel convenient for everyone by facilitating the accessibility features.
Chapter 3- India’s Industry Sector
- PM GatiShakti National Master Plan is aimed at integrated infrastructure development.
- It has broadly two components to achieve integration, synchronisation, prioritisation, and optimization-
- The development of GIS-based technology platform called National Master Plan, wherein everything is linked from roads to railways, from aviation to agriculture, various ministries and departments.
- The administrative arrangement to integrate efforts of various line ministries/ departments for synchronised development of multimodal infrastructure and the economic zone through the formation of a three-tier institutional arrangement.
National Logistics Policy
- The National Logistics Policy (NLP) was launched in 2022.
- The policy complements the PM GatiShakti National Master Plan.
- While Master Plan is aimed at integrated infrastructure development, the National Logistics Policy aims to bring efficiency to logistics services, and human resources throughChapter 3- streamlining processes, a regulatory framework, skill development, mainstreaming logistics in higher education, and the adoption of suitable technologies.
Foreign Direct Investment Policy
- DPIIT was the nodal department for the formulation of the policy on Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- It is also responsible for maintenance and management of data on inward FDI into India, based on the remittances reported by the Reserve Bank of India.
Make in India
- The ‘Make in India’ initiative was launched in 2014.
- It aims to facilitate investment, foster innovation, build best-in-class infrastructure, and make India a hub for manufacturing, design, and innovation.
- It is one of the unique ‘Vocal for Local’ initiatives that promotes India’s manufacturing domain to the world.
- The initiative has significant achievements and presently focuses on 27 sectors under Make in India 2.0.
Production Linked Incentive Scheme
- To make India ‘Atmanirbhar’, Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes for 14 key sectors were announced with an outlay of Rs 1.97 lakh crore to enhance India’s manufacturing capabilities and exports.
- The PLI schemes have major objectives that include: attracting investments in sectors of core competency and cutting-edge technology; make Indian companies and manufacturers globally competitive so that they can penetrate global markets and integrate with global value chains.
Startup India
- It was launched in 2016.
- The initiative aims to foster entrepreneurship and promote innovation by creating an ecosystem conducive to startup growth.
- It strives to provide an impetus to the entrepreneurial setup across three major pillars i.e., (i) simplification and handholding, (ii) funding support and incentives, and (iii) industry-academia partnership and incubation.
- As of 15 May 2023, a total of 99,371 startups have been recognised by DPIIT.
- DPIIT has also established Fund of Funds (FFS) with a corpus of INR 10,000 crore, to meet the funding needs of startups.
Heavy Industries
- The Ministry of Heavy Industries promotes the development and growth of automobile, capital goods and heavy electrical equipment sectors.
- It also administers 29 Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) engaged in manufacturing, consultancy and contracting services and four autonomous organisations.
- It aims at transforming mobility in the country by increasing competitiveness of the domestic automobile industry and promoting advanced technology and sustainable and affordable electric mobility solutions for the citizens.
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- It has emerged as a highly vibrant and dynamic sector of the Indian economy over the last seven decades.
- The primary responsibility of promotion and development of MSMEs is of the state governments. However, the Government of India supplements the efforts of the states through various initiatives.
- MSMEs are classified into following:
- Micro enterprise- investment in plant and machinery or equipment does not exceed one crore rupees and turnover does not exceed five crore rupees;
- Small enterprise- investment in plant and machinery or equipment does not exceed ten crore rupees and turnover does not exceed fifty crore rupees; and
- Medium enterprise- investment in plant and machinery or equipment does not exceed fifty crore rupees and turnover does not exceed two hundred and fifty crore rupees.
- The Ministry of MSME also launched Udyam Assist Platform in January, 2023 to bring Informal Micro Enterprises under the formal ambit of MSMEs.
Indian MSME Sector
- It contributes to around 27 per cent of India’s GDP, around 44 per cent of India’s exports and providing employment to over 11.10 crore people.
- MSME sector is also important for fostering entrepreneurship and generating self-employment opportunities at comparatively lower capital cost, next only to agriculture.
Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC)
- It was established under the Act of Parliament, and as amended in 1987 and 2006.
- It is a statutory organisation under the Ministry of MSME.
- It is engaged in promoting and developing Khadi and Village Industries (KVI) for providing employment opportunities in the rural areas, thereby strengthening the rural economy.
Textiles
- It is one of the largest in the world, with a large raw material base and manufacturing strength across the value chain.
- Traditional sectors like handlooms, handicrafts and small scale powerloom units are the biggest source of employment for millions of people in rural and semi-urban areas.
- The textile industry has inherent linkages with agriculture, culture and traditions of the country.
- The textile industry contributes to 7 percent of industry output in value terms of 2 percent of India’s GDP and to 15 percent of the country’s export earnings.
- With over 45 million people employed directly, this industry is one of the largest sources of employment generation in the country.
Steel
- India’s crude steel capacity has steadily risen to 142 MT at present following which India has become the world’s second-largest producer of crude steel, surpassing Japan.
- The crude steel production capacity has steadily risen to 161.30 MT.
- A vibrant domestic steel industry is important for developing economy as it is a critical input across major sectors such as construction, infrastructure, automotive, capital goods, defence, rail, etc.
Fertilisers
- Department of Fertilisers comes under the ambit of the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers.
- The main objective of the Department is to ensure adequate and timely availability of fertilisers at affordable prices for maximising agricultural production in the country.
- Its functions include planning, promotion and development of the fertilisers industry, planning and monitoring of production; import and distribution of fertilisers and management of financial assistance by way of subsidy/concession for indigenous and imported fertilisers.
- The Department has one attached office under it, viz., Fertilisers Industry Coordination Committee (FICC ).
- It also administers 9 Fertiliser Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs).
Chemicals and Petro-chemicals
- Department of Chemicals and Petro-chemicals was transferred to the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers.
- The Department is entrusted with the responsibility of planning, development and regulations of the chemicals, petro-chemicals and pharmaceutical industry sector, including: drugs and pharmaceuticals, excluding those specifically allotted to other departments; insecticides, excluding the administration of the Insecticides Act, 1968; molasses; alcohol - industrial and potable from the molasses route; all organic and inorganic chemicals not specifically allotted to any other ministry or department; petrochemicals; synthetic rubber; and planning, development and control of, and assistance to, all industries dealt with by the Department.
Pharmaceuticals
- The Indian pharmaceutical industry is the world’s third-largest by volume.
- Total Annual Turnover of Pharmaceuticals industry is Rs 3,79,450 crore for 2022- 2023.
- In the last nine years, the sector has grown steadily by CAGR of 6.4 per cent (as per total pharma export).
- Total exports of pharmaceuticals are to the tune of Rs 1,94,254 crore and total imports of pharmaceuticals are to the tune of Rs 56,391 crore for 2022-23.
Geological Survey of India (GSI)
- It is a premier earth science organisation of the country, is the principal provider of basic earth science information to the Government, industry, and the geoscientific sector.
- It was started in 1851 as a department engaged primarily in research for coal and other earth minerals.
- GSI is now the custodian of one of the largest and most comprehensive earth science databases developed over the century and a half.
- The present activity domains of GSI include surface mapping; aerial and remote sensing surveys; offshore surveys; exploration for mineral and energy resources; engineering geology; geotechnical investigations; geoenvironmental studies; geology of water resources; geohazard studies; research and development; training and capacity building; and information services, etc.
Indian Bureau of Mines
- It was established in March 1948, as a multidisciplinary scientific and technical organisation under the Ministry of Mines with statutory and developmental responsibilities for conservation and systematic exploitation of mineral resources other than coal, petroleum, natural gas, atomic minerals and minor minerals.
- It also undertakes scientific, techno-economic, and research-oriented studies in various aspects of mining, geological studies, ore beneficiation and environmental studies.
- The Ministry of Mines has three Public Sector Undertaking (PSUs) under its administrative control. National Aluminium Company Limited (NALCO ), Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL) are operating in the field of mining and mineral processing, and Mineral Exploration Corporation Limited (MECL) is operating in the field of mineral exploration.
Chapter 4- Agriculture and Rural Development
- Livelihood security and financial empowerment of rural people are key priorities of the Government of India in its path towards Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare has been allocated Rs1,25,036 crore for FY 2023-24, 5 per cent higher than the revised estimates for 2022-23.
- Budget provisions were made for development of Digital Public Infrastructure and to set-up an Agriculture Accelerator Fund.
- The target for agriculture credit was increased to Rs 20 lakh crore and a provision of Rs 6,000 crore was made to launch a new scheme PM Matsya Sampada Yojana.
Raising the Bar
- India has set a new record for both food grain and horticultural production in 2022-23 with an estimated production of 330 million tonnes and 352 million tonnes respectively.
- While foodgrain production touched an increase of over 4 percent (14 million tonnes), the output of horticultural produce showed an increase of over 1 percent (5 million tonnes) compared to the previous year.
- Chief food grains, paddy (rice), and wheat recorded an all-time high production in 2022-23 (July-June cycle) at 135 million tonnes and 110 million tonnes respectively.
- Among horticultural crops, fruit production stood at 108 million tonnes, and vegetables reported a record production of 213 million tonnes.
- Government announced the increase in MSP for mandated Rabi crops for marketing season 2024-25.
- In absolute terms, the highest increase in MSP has been announced for lentils at Rs 425 per quintal. This was followed by rapeseed and mustard (Rs 200/quintal); wheat and safflower (Rs 150/quintal); and barley and gram (Rs 115 & Rs 105/quintal respectively).
Initiatives for Growth
- Government has approved the ‘PM Programme for Restoration, Awareness Generation, Nourishment, and Amelioration of Mother-Earth’ (PM-PRANAM) scheme.
- The initiative aims to support the mass movement started by States/ Union Territories to save the health of Mother Earth by promoting sustainable and balanced use of fertilisers, adopting alternate fertilisers, promoting alternate farming, and implementing resource conservation technologies.
- The launch of the world's first Nano-DAP liquid (Di-Ammonium Phosphate) had been a momentous achievement (26 April 2023).
- Nano-DAP and Nano-Urea (Liquid) are patented items poised to bring a paradigm shift in the agriculture sector.
- Nearly 6.3 crore bottles have been produced till March 2023. The effect of one bottle of 500 ml on the crop is equivalent to that of a 45 kg bag of granular urea.
- India organised a G20 Agriculture Ministers’ Meeting in Hyderabad (15 to 17 June 2023).
- The two key outcomes of the meeting: (i) Deccan High Principles on Food Security and Nutrition 2023, and (ii) International Millets and Other Ancient Grains Research Initiative (MAHARISHI).
- To promote digital transactions in rural areas, the Ministry of Rural Development has launched a campaign, ‘Promoting Digital Transactions in 50,000 Gram Panchayats’, under the ‘Amrit Mahotsav’ in Lucknow.
- Jal Jeevan Mission has achieved the milestone of providing tap water connections to 13 crore households.
- Government has approved an extension of the PM Ujjwala Yojana for the release of 75 lakh LPG connections over three years (2023-24 to 2025-26).
- The PM Gram Sadak Yojana has helped create 1,77,119 number of roads measuring 7,45,780 km under all its verticals/interventions.
- The inclusion of various IT mechanisms has accelerated the implementation of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Empowerment Guarantee Act, 2005 with greater transparency. As per records, it has created 201.96 crore person days and 14.35 crore active workers during 2023-24.
- Mission Amrit Sarovar is aimed at rejuvenation and development of 75 water bodies in each district of the country. So far, over 67,000 such sarovars have been constructed, while over 1.10 lakh sites have been identified.
- This year marks nine years of the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM), and the achievement of 75% ODF (Open Defecation Free) Plus villages is a significant milestone in this regard.
- The Government continued its emphasis on improving the quality of life in rural areas to ensure more equitable and inclusive development. It aims to ‘transform lives and livelihoods through proactive socio-economic inclusion, integration, and empowerment of rural India’.
Mains Practice Question:- (in around 250 words)
Q1. Explain the meaning of investment in an economy in terms of capital formation. Discuss the factors to be considered while designing a concession agreement between a public entity and private entity.
Q2. The G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration is a comprehensive document as it lays the roadmap for collective global action in building a prosperous future. Discuss.
Q3. Farm sector and farmers continue to suffer losses despite having several measures to reduce the vulnerability of farmers in India. Suggest some measures that can be taken to improve their conditions.
QUICK LINKS